110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

硫辛酸可降低糖尿病大鼠多聚 ADP-核糖聚合酶的表达并抑制其细胞凋亡
Authors Chen J, Li Q
Received 10 December 2019
Accepted for publication 27 April 2020
Published 20 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1725—1731
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S241678
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
Purpose: To study the effects of lipoic acid on poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) expression and apoptosis in diabetic rats.
Materials and Methods: Sprague–Dawley rats (n=30) with high-fat diet- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes were randomly divided into two groups: diabetic model (DM) group and lipoic acid (LA) treatment group; another 10 rats were selected as normal controls (NC). The serum levels of 8-hydroxy-2ʹ-deoxyguanosine, nitrotyrosine, and 8-isoprostane; sciatic nerve cell apoptosis index; and PARP expression were detected in the rats, and morphological changes in the sciatic nerve were recorded.
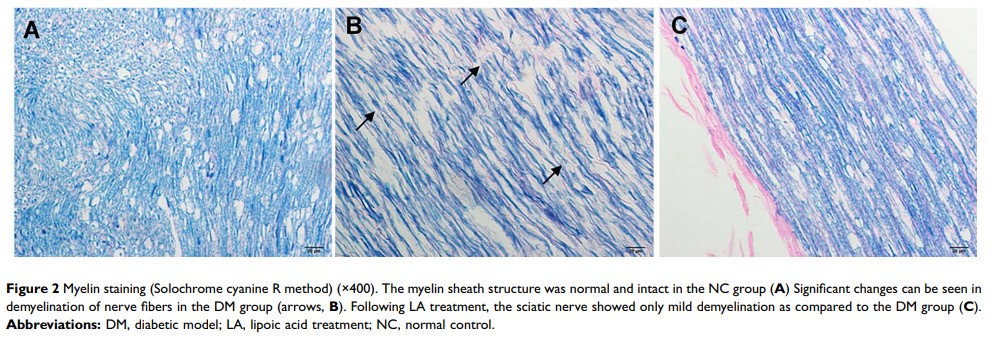
Results: The blood glucose level in the DM and LA groups was significantly higher than that of the NC group (P< 0.01). Compared to the NC group, the DM group showed demyelinating changes to sciatic nerve fibers. PARP expression; serum levels of 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine, nitrotyrosine, and 8-isoprostane; and the apoptosis index of sciatic nerve cells were significantly higher than those of the NC group (P< 0. 01). Following LA treatment, the above indices showed significant improvement (P< 0.01).
Conclusion: Lipoic acid may improve the symptoms of diabetic neuropathy by reducing PARP activity and inhibiting apoptosis.
Keywords: lipoic acid, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, poly ADP-ribose polymerase, oxidative stress, apoptosis