110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

含 CUB 域蛋白 1 促进宫颈癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Huang L, Chen Y, Lai S, Guan H, Hu X, Liu J, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Zhou J
Received 26 November 2019
Accepted for publication 27 March 2020
Published 21 May 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 3759—3769
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S240107
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Xueqiong Zhu
Purpose: Emerging evidence have revealed significant contributions of CUB domain-containing protein-1 (CDCP1) in tumorigenesis, including colon, renal, ovarian, pancreatic, prostate and breast cancers. However, the roles of CDCP1 in cervical cancer (CC) still remain elusive.
Materials and Methods: Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, immunohistochemistry and Western blotting were used to confirm the expression of CDCP1 in CC tissues compared with matched non-tumor tissues. In vitro, gain-of-function and loss-of-function studies were used to investigate the biological function and underlying mechanism of CDCP1 in cervical carcinogenesis. Furthermore, tumor growth was evaluated using a xenogenous subcutaneously implant model of CC cells in vivo.
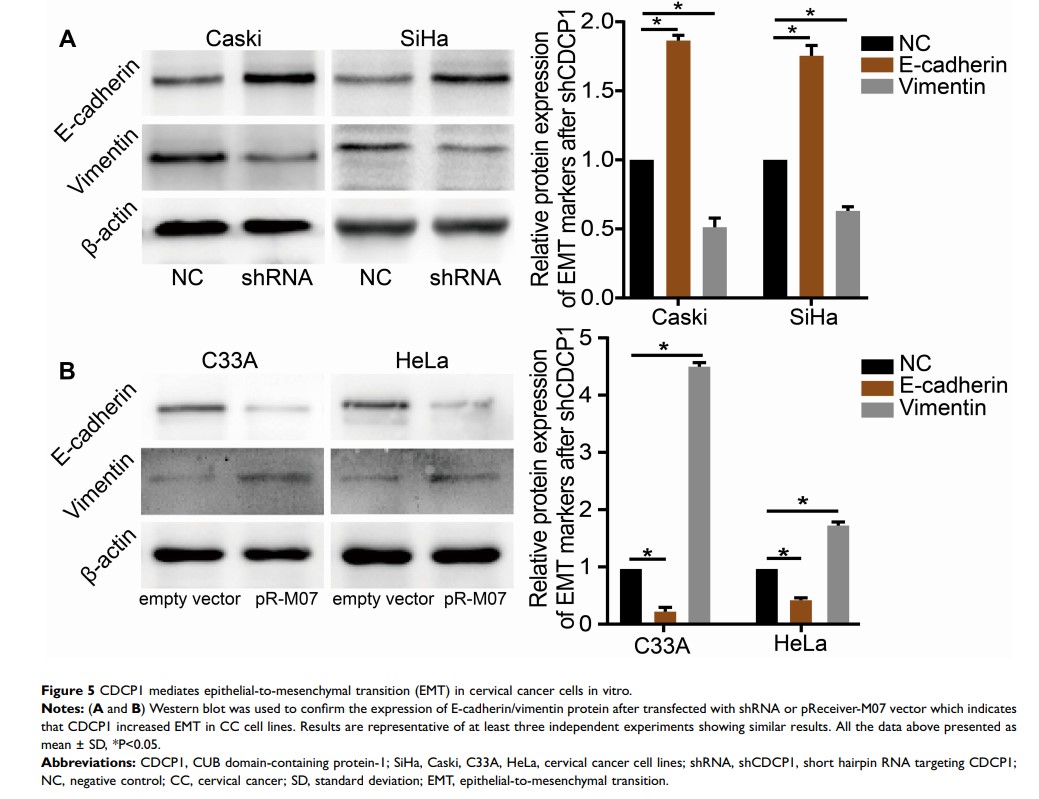
Results: Here, we confirmed that CDCP1 was significantly increased in human CC both in mRNA and in protein levels compared to normal cervical tissues. Furthermore, we demonstrated that increased CDCP1 expression promotes proliferation, migration, invasion and mediates the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition phenotype in HeLa and C33A cells. Also, CDCP1 knockdown reverses all the effects of enhanced CDCP1 on cell behavior in SiHa and Caski cells. Importantly, the suppressive expression of CDCP1 repressed tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model of CC.
Conclusion: In summary, our current study results provide novel insights into the role of CDCP1 in CC progression. Potentially, CDCP1 might serve as a diagnostic biomarker and a novel therapeutic target for CC.
Keywords: cervical carcinoma, CDCP1, EMT, tumor metastasis