110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

糖化血红蛋白 A1c 改善了列线图的性能,可预测 2 型糖尿病的 5 年患病率
Authors Ma CM, Yin FZ
Received 7 March 2020
Accepted for publication 30 April 2020
Published 21 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1753—1762
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S252867
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Juei-Tang Cheng
Aim: To develop and validate a model, which combines traditional risk factors and glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) for predicting the risk of type 2 diabetes (T2DM).
Materials and Methods: This is a historical cohort study from a collected database, which included 8419 males and 7034 females without diabetes at baseline with a median follow-up of 5.8-years and 5.1-years, respectively. Multivariate cox regression analysis was used to select significant prognostic factors of T2DM. Two nomograms were constructed to predict the 5-year incidence of T2DM based on traditional risk factors (Model 1) and traditional risk factors plus HbA1c (Model 2). C-index, calibration curve, and time-dependent receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve were conducted in the training sets and validation sets.
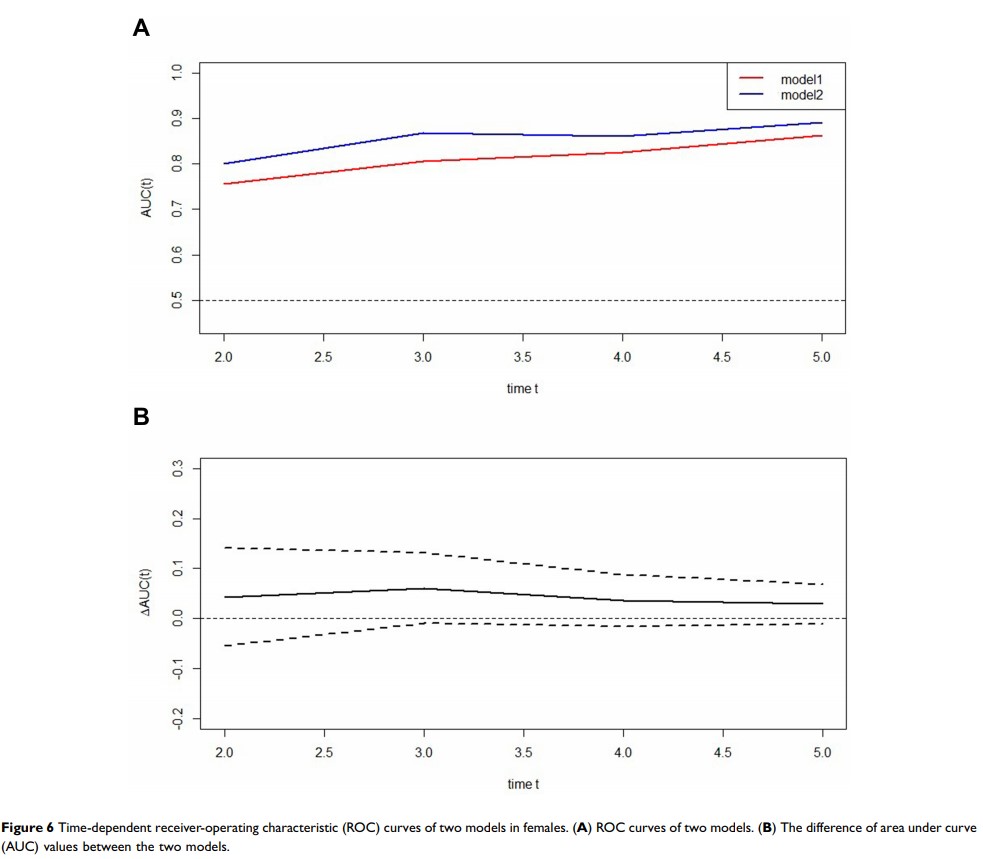
Results: In males, the C-index was 0.824 (95% CI: 0.795– 0.853) in Model 1 and 0.867 (95% CI: 0.840– 0.894) in Model 2; in females, the C-index was 0.830 (95% CI: 0.770– 0.890) in Model 1 and 0.856 (95% CI: 0.795– 0.917) in Model 2. The areas under curve (AUC) in Model 2 for prediction of T2DM development were higher than in Model 1 at each time point. The calibration curves showed excellent agreement between the predicted possibility and the actual observation in both models. The results of validation sets were similar to the results of training sets.
Conclusion: The proposed nomogram can be used to accurately predict the risk of T2DM. Compared with the traditional nomogram, HbA1c can improve the performance of nomograms for predicting the 5-year incidence of T2DM.
Keywords: type 2 diabetes, nomogram, risk factor, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c