110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-381 可通过靶向 STC2 介导头颈部鳞状细胞癌的进展
Authors Ma HF, Lv GX, Zhang DH
Received 16 January 2020
Accepted for publication 28 April 2020
Published 21 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 4485—4493
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S246289
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
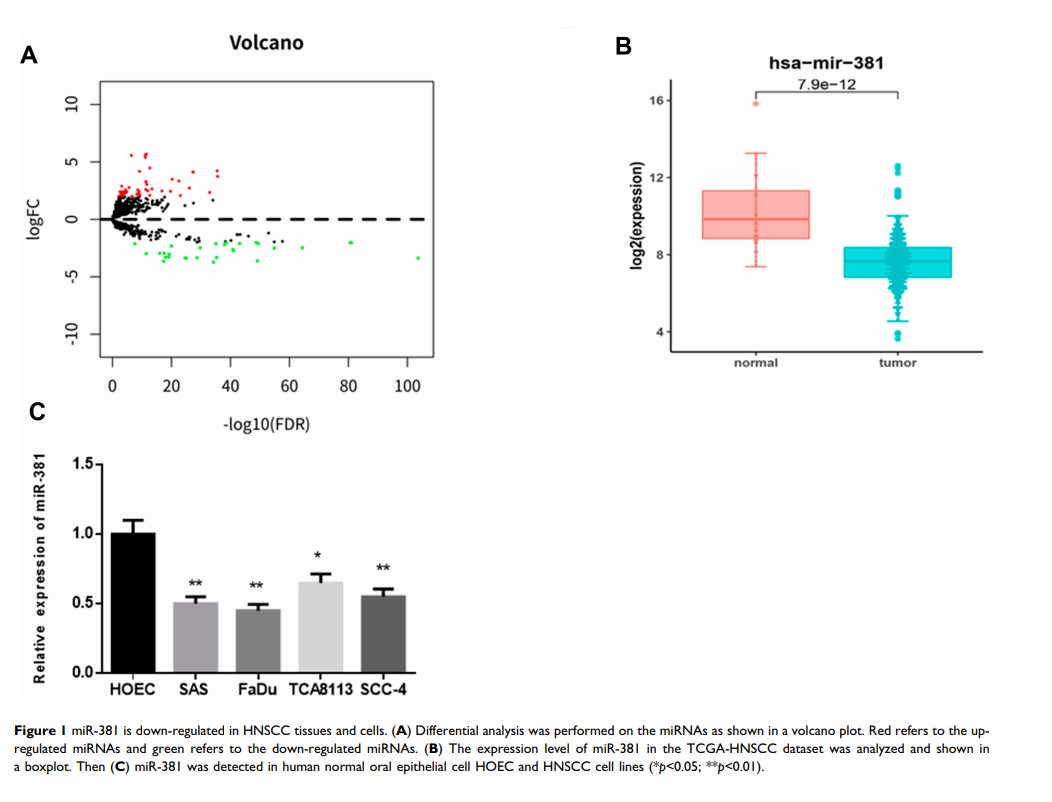
Objective: miR-381 is implicated in the occurrence and development of various cancers, yet its role in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remains largely unknown. This study sought to research the direct target of miR-381 in HNSCC and investigate their roles in cancer progression.
Methods: miRNA and mRNA expression files of HNSCC were accessed from TCGA database and then processed for differential analysis. Bioinformatics databases were employed to predict the target mRNAs of the potential miRNA. qRT-PCR was conducted to determine the expression levels of the target miRNA and mRNA. Then, a series of in vitro experiments like CCK-8, colony formation assay, wound healing assay and transwell assay were performed to detect cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay was carried out for the further validation of the targeted relationship between the miRNA and mRNA.
Results: miR-381 was observed to be greatly down-regulated in HNSCC cells, and its overexpression could inhibit cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Besides, dual-luciferase reporter gene assay confirmed that STC2 was a direct target of miR-381, and their expression levels were reversely correlated. Moreover, rescue experiments demonstrated that overexpressing STC2 could rescue the inhibitory effect of miR-381 overexpression on cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Also, we verified that miR-381/STC2 exerted its function on HNSCC proliferation by mediating the FAK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.
Conclusion: miR-381 suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in HNSCC through targeting STC2, and participates in HNSCC development probably via the FAK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.
Keywords: miR-381, STC2, FAK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, HNSCC