110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA HAND2-AS1 通过靶向 miR-106a-5p/RBM24 轴来调节前列腺癌细胞的生长
Authors Wei P, Yang J, Zhang D, Cui M, Li L
Received 16 January 2020
Accepted for publication 7 April 2020
Published 21 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 4523—4531
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S246274
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
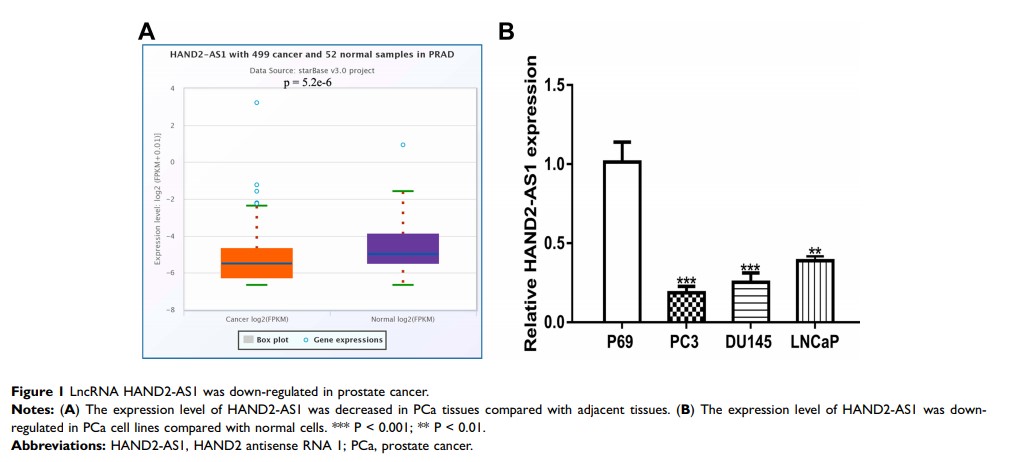
Introduction: Increasing evidence has shown that abnormally expressed long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) plays crucial roles in prostate cancer (PCa) progression.
Materials and Methods: Here, we analyzed the expression level of lncRNA HAND2 antisense RNA 1 (HAND2-AS1) in PCa cells and tissues. Function assays were performed to investigate the biological roles of HAND2-AS1 in PCa cell behaviors. Bioinformatics methods, luciferase activity reporter assay, and RNA pull-down assay were performed to validate the connection of microRNA-106a-5p (miR-106a-5p) with HAND2-AS1. Also, the target of miR-106a-5p was explored using the same methods.
Results: Our results revealed HAND2-AS1 expression was decreased in both PCa cells and tissues. In vitro functional assays showed HAND2-AS1 could inhibit PCa cell proliferation and colony formation through promoting cell apoptosis. Dual-luciferase activity assays showed miR-106a-5p could directly bind with HAND2-AS1 and RNA binding motif protein 24 (RBM24). Mechanistically, we showed that HAND2-AS1 regulates PCa cell behaviors via targeting miR-106a-5p/RBM24 axis.
Conclusion: In summary, our results illustrated that HAND2-AS1 functions as miR-106a-5p sponge to regulate RBM24 expression, and to influence PCa progression.
Keywords: HAND2-AS1, miR-106a-5p, RBM24, prostate cancer