110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ALK G1202R 突变和 LIPI-NTRK1 重排的肺腺癌患者的布加替尼原发性耐药
Authors Xiao Z, Huang X, Xie B, Xie W, Huang M, Lin L
Received 13 February 2020
Accepted for publication 6 May 2020
Published 22 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 4591—4595
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S249652
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Purpose: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK ) inhibitors have transformed the management of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with ALK gene rearrangement. This paper reports a new resistance mechanism to a second-generation ALK inhibitor, brigatinib.
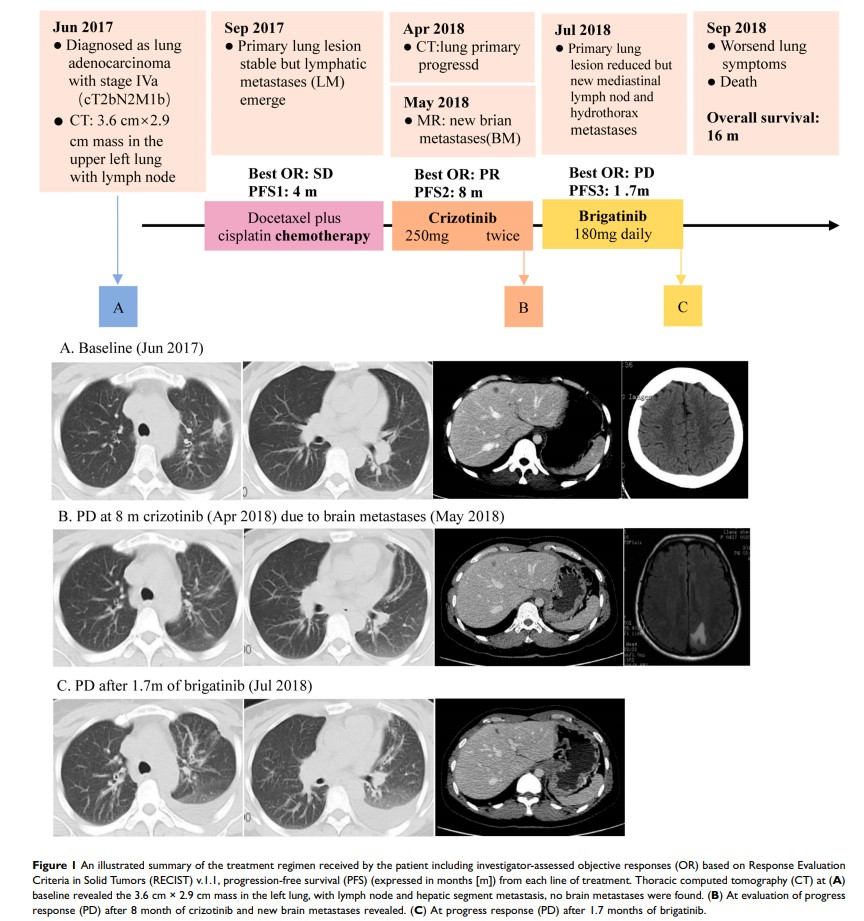
Case Report: A 43-year-old woman who had no history of smoking was diagnosed with stage IVa (T2bN2M1b) lung adenocarcinoma. After the first-line chemotherapy failed, the patient received crizotinib due to the presence of EML4-ALK fusion by next-generation sequencing (NGS). The patient had disease progression after 8 months on crizotinib, and a second NGS identified the ALK G1202R resistance mutation. Therefore, she was switched to brigatinib. After only 53 days of treatment with brigatinib, the patient developed a new 1.6× 1.2 cm lesion in the mediastinal lymph node. A third NGS testing revealed a new form of NTRK rearrangement (LIPI-NTRK1 ). The patient died 16 months after diagnosis.
Conclusion: This paper provides new insights into the primary resistance to brigatinib in NSCLC patients carrying ALK G1202R mutation. The new fusion form of NTRK rearrangement was detected, which may provide potential treatment options after brigatinib resistance.
Keywords: NTRK1, ALK, primary resistance, brigatinib, NSCLC