110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA SNHG16 通过介导 miR-877-5p/FOXP4 轴促进喉鳞状细胞癌的进展
Authors Wang X, Liu L, Zhao W, Li Q, Wang G, Li H
Received 21 February 2020
Accepted for publication 26 April 2020
Published 22 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 4569—4579
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S250752
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Objective: Laryngeal cancer is a common malignant tumor in the ENT, of which laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) accounts for more than 90% of laryngeal cancer. The purpose of this study is to investigate the regulatory mechanism of lncRNA SNHG16 in LSCC.
Materials and Methods: Real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to measure mRNA expression. Cell Counting Kit (CCK-8), Transwell and luciferase reporter assays, flow cytometric analysis and Western blot analysis were used to investigate the function of lncRNA SNHG16 in LSCC.
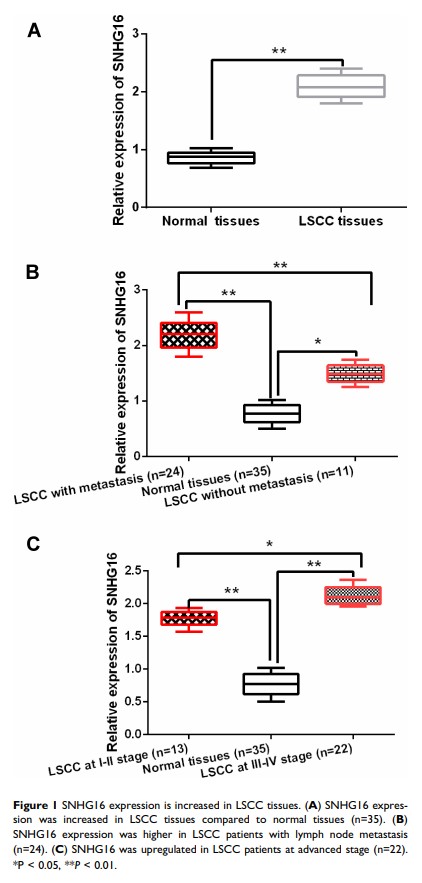
Results: SNHG16 expression was increased in LSCC tissues and cells. The abnormal expression of SNHG16 was associated with clinical stage and lymph node metastasis in LSCC patients. In addition, knockdown of SNHG16 restrained cell proliferation, migration and invasion in LSCC. More importantly, SNHG16 acted as a competitive endogenous RNA in LSCC and regulated FOXP4 expression by making miR-877-5p sponge. Further, SNHG16 promoted LSCC progression by interacting with miR-877-5p and FOXP4.
Conclusion: LncRNA SNHG16 promotes the progression of LSCC by sponging miR-877-5p and upregulating FOXP4.
Keywords: SNHG16, laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, miR-877-5p, FOXP4