110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

青春期小鼠社交挫败压力对少突胶质细胞谱系细胞和神经炎性介质的长期影响
Authors Xu Y, Fang Z, Wu C, Xu H, Kong J, Huang Q, Zhang H
Received 29 January 2020
Accepted for publication 30 April 2020
Published 22 May 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 1321—1330
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S247497
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jun Chen
Objective: Adverse childhood and adolescent experiences are associated with the emergences of psychopathology later in life and have negative consequences on white matter integrity. However, this adversity-induced white matter impairment remains not fully investigated.
Methods: Adolescent Balb/c mice were subjected to intermittent social defeat stress once a day during postnatal days 25 to 40. Then, the subjects were allowed to recover for three weeks before sacrifice. At the end, oligodendrocyte (OL) lineage cells, cell proliferation, and microglia activation, as well as myelin basic protein (MBP) levels in frontal cortex and hippocampus were evaluated. The levels of interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 in the brain regions were assessed.
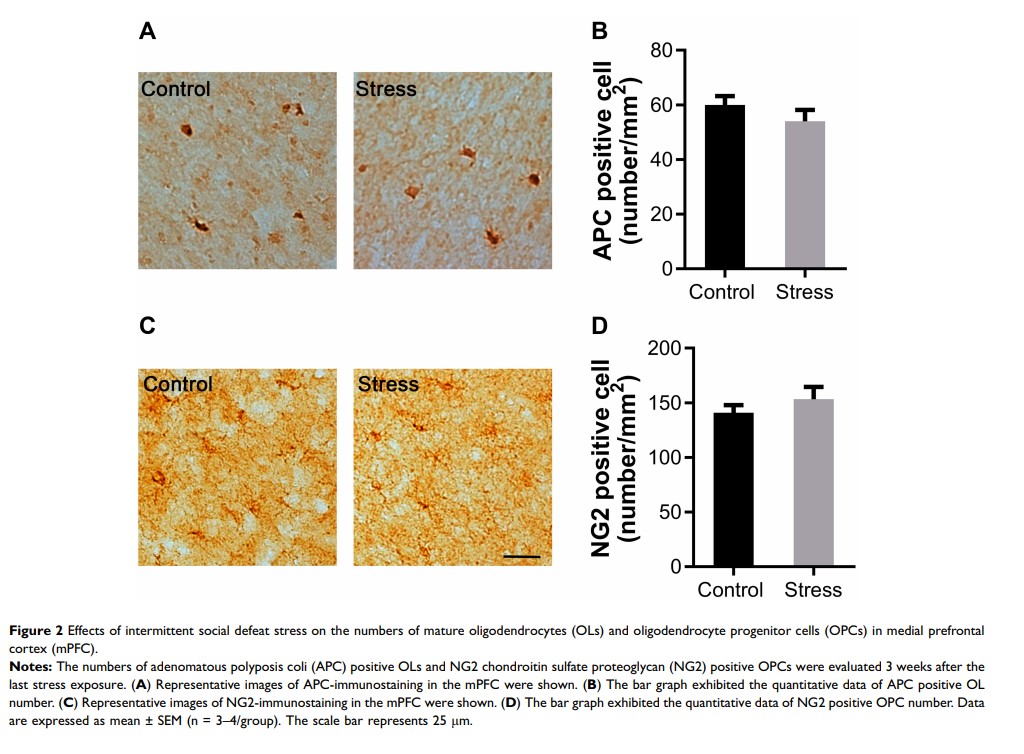
Results: MBP protein level in frontal cortex, but not in the hippocampus of defeated mice, decreased significantly compared to controls. The numeral densities of mature OLs, oligodendrocyte progenitor cells, and proliferating cells in medial prefrontal cortex were comparable between the defeated mice and controls. The defeated mice, however, showed significantly higher IL-1β level, although IL-6 level and numeral density of microglia in frontal cortex did not change relative to controls.
Conclusion: These results indicate that effects of intermittent social defeat stress on the white matter integrity and OL lineage cells in mouse brain are region- and developmental stage-specific. Upregulated IL-1β may contribute to this negative consequence though the underlying mechanism remains to be investigated.
Keywords: social defeat stress, adolescence, myelin, oligodendrocyte lineage cells, interleukin-1β