110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

bla KPC-2 和 Mcr-3.3 基因并存于分离自腹泻病患者的豚鼠气单胞菌 SCAc2001中
Authors Tang L, Huang J, She J, Zhao K, Zhou Y
Received 10 January 2020
Accepted for publication 23 April 2020
Published 25 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1527—1536
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S245553
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eric Nulens
Purpose: To characterize the genetic feature of a multi-drug-resistant Aeromonas caviae strain isolated from the diarrhea sample of a 45-year-old male patient with acute diarrhea.
Materials and Methods: Whole-genome of the A. caviae strain SCAc2001 was sequenced via the Illumina system, followed by a series of bioinformatic analyses to describe the genetic feature.
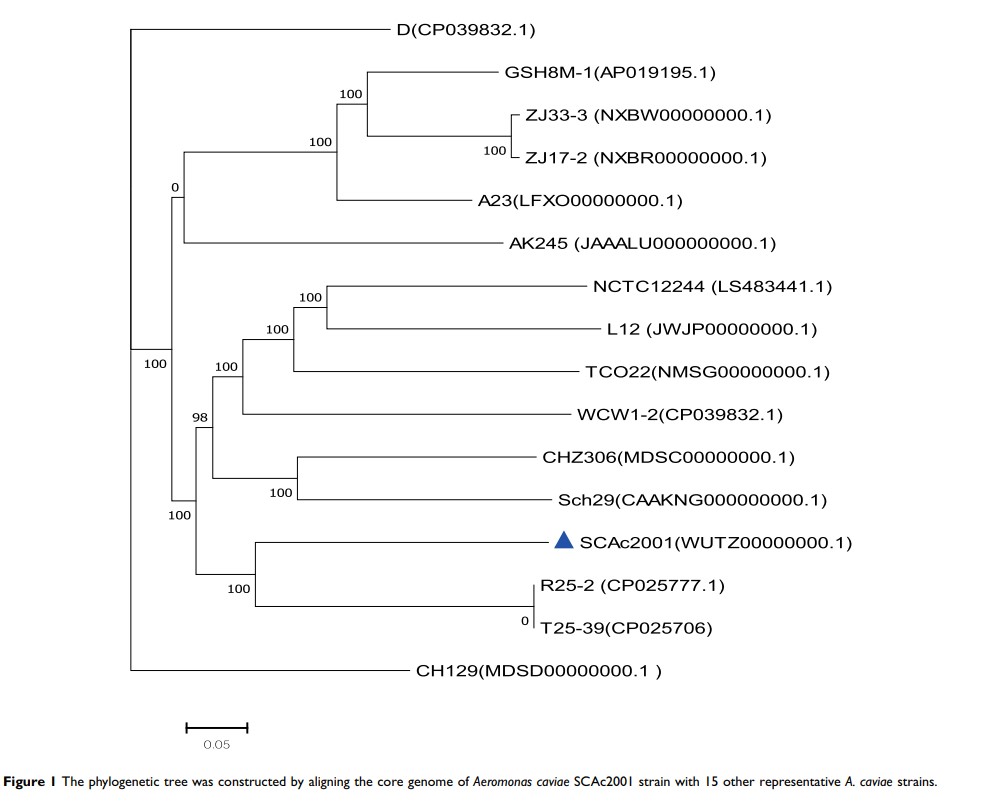
Results: The genome sequence of A. caviae SCAc2001 was assembled into 340 scaffolds (305 of them were > 1000 bp in length and 4,487,370 bp in total) with an average G+C content of 61.09%. Phylogenetic analysis showed that the A. caviae SCAc2001 strain was highly similar to the A. caviae strain R25-2 and T25-39. Resistome analysis identified that A. caviae SCAc2001 carried 13 antimicrobial resistance genes, including β-lactams (bla KPC, bla CTX-M-14, bla TEM-1, bla OXA-10, bla OXA-427, bla VEB-3 and bla MOX-6), aminoglycosides (aadA1 ), fluoroquinolones (aac(6 ʹ )-Ib-cr ), phenicol resistance (catB3 ), sulfonamide (sul1 ), trimethoprim (dfrA5 ) and colistin resistance (mcr-3.3 ).And also, A. caviae ScAc2001 carried 54 putative virulence genes including the type IV pilus, fimbria, flagellarthe, and hemolysin A encoding genes, and 12 pathogen–host interactions (PHI) genes. There were also four genomic islands and eight prophages in the genome of A. caviae ScAc2001. In addition, A. caviae SCAc2001 also carried three secondary metabolism products coding clusters including nonribosomal peptide synthetases (nrps), hserlactone and bacteriocin.
Conclusion: A. caviae ScAc2001 carries many resistance genes, a variety of virulence factors, PHI genes and four genomic islands and eight prophages, which poses a severe threat to infectious diseases control strategies, diagnosis methods and clinical treatment.
Keywords: Aeromonas caviae , bla KPC-2, mcr-3.3 , virulence factors, secondary metabolism products