110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

甘氨酸通过 miR-19a-3p/AMPK/GSK-3β/HO-1 信号通路改善缺血性卒中
Authors Chen ZJ, Zhao XS, Fan TP, Qi HX, Li D
Received 2 February 2020
Accepted for publication 27 April 2020
Published 25 May 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 2021—2031
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S248104
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yan Zhu
Purpose: To explore the molecular mechanism of glycine in improving ischemic stroke.
Patients and Methods: The serum samples of patients with ischemic stroke and healthy people were compared. The ischemic stroke model of PC12 cells was established by oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD). qPCR quantified miR-19a-3p and AMPK mRNA, and protein expression was detected by Western blot. MTT was used to detect cell activity. Flow cytometry was used to detect cells. Glucose metabolism kit was used to detect glucose intake and formation amount of lactic acid.
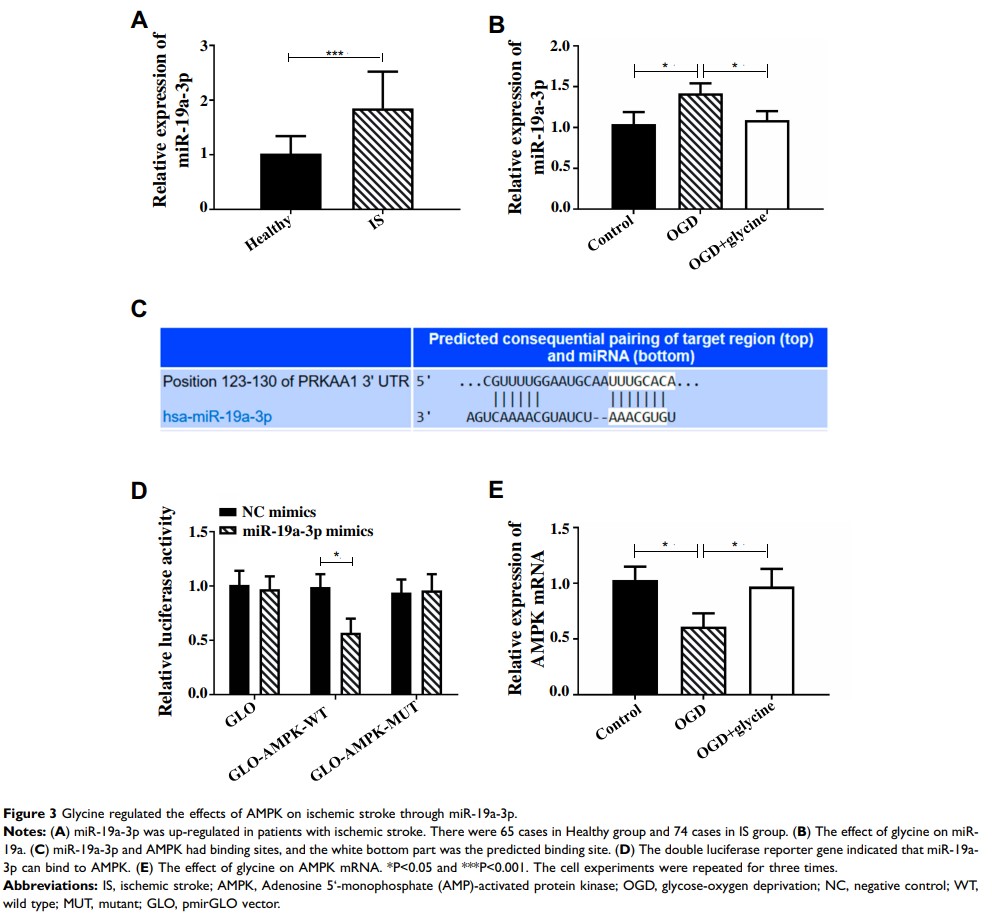
Results: Compared with the control group, OGD group (OGDG) showed lower cell activity and increased cell apoptosis. TNF-α, IL-1βI, L-6, Caspase 3, Caspase 9 and Bax were up-regulated, and Glut1, HK2, LDHA, PDK1, PKM2 and Bcl2 were down-regulated. At the same time, glucose intake, formation amount of lactic acid and cell apoptosis rate were reduced, and AMPK/GSK-3β/HO-1 pathway activity was down-regulated. Glycine could counteract the above phenomena in OGDG. miR-19a-3p and AMPK decreased and increased, respectively, during glycine therapy. AMPK was the target gene of miR-19a-3p. Rescue experiments demonstrated that glycine improved cell apoptosis, inflammatory response and glucose metabolism disorder of ischemic stroke through miR-19a-3p/AMPK/GSK-3β/HO-1 pathway.
Conclusion: Glycine improves ischemic stroke through miR-19a-3p/AMPK/GSK-3β/HO-1 pathway.
Keywords: ischemic stroke, AMPK/GSK-3β/HO-1 pathway, miR-19a-3p, glycine