110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

circMTO1 过表达通过 miR-9-5p/NOX4 轴对肝癌细胞增殖和凋亡的调控作用机制
Authors Wang J, Tan Q, Wang W, Yu J
Received 1 December 2019
Accepted for publication 27 April 2020
Published 26 May 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 3915—3925
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S240719
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Purpose: To investigate the potential role of the circMTO1/miR-9-5p/NOX4 axis in liver cancer.
Materials and Methods: Human genome-wide circrna microarray V2 was used for analyzing the expression profile of circRNAs in human tissue samples. The TargetScan database was used to predict target genes. Gene overexpression and silencing in hepatoma cell lines were achieved by transfecting the cells with suitable constructs. Quantitative real time PCR and Western blotting were used to analyze gene and protein expression levels. CCK-8 analysis was performed to detect cell proliferation and the transwell assay for analyzing cell migration. Annexin V-FITC/PI staining and immunohistochemistry were respectively used to detect apoptosis and protein expression.
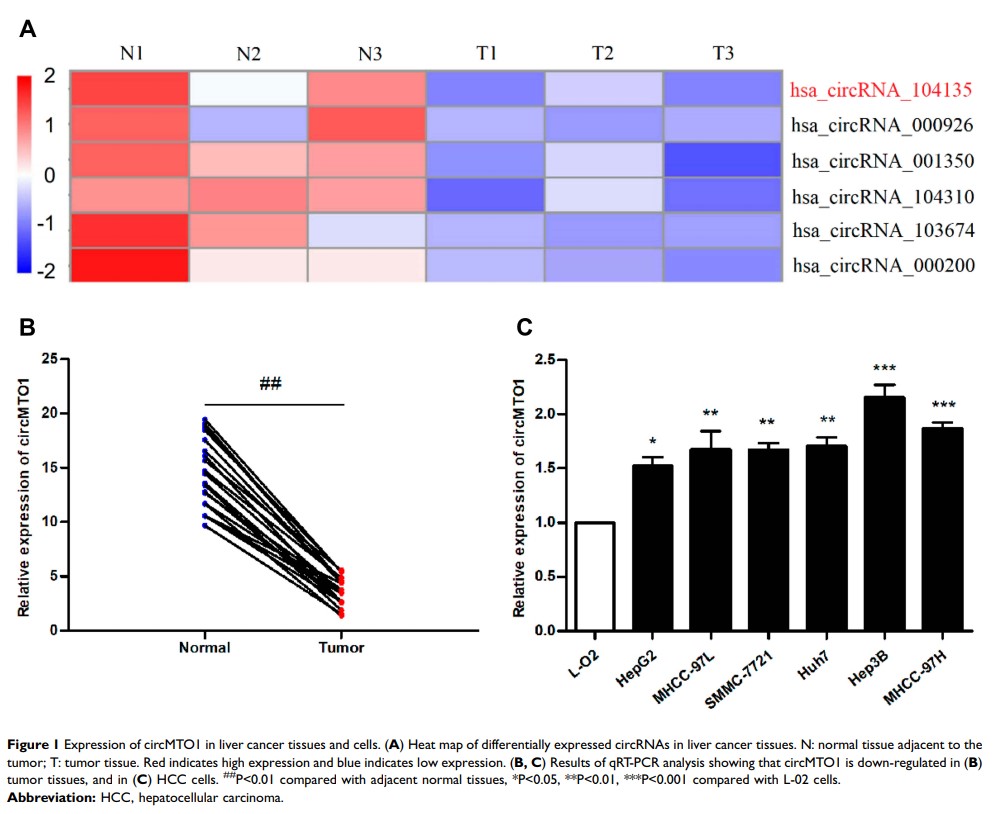
Results: CircMTO1 were down-regulated in the liver cancer tissues and cell lines compared to their respective normal controls. TargetScan database screening and dual luciferase assay revealed that circMTO1 was a molecular sponge of miR-9-5p, and NOX4 was the target gene of miR-9-5p. Overexpression of circMTO1 and NOX4 inhibited proliferation and migration of hepatoma cells, while the overexpression of miR-9-5p had the opposite effects. In contrast, overexpression of circMTO1 and NOX4 promoted apoptosis, while that of miR-9-5p decreased the cell apoptosis rates.
Conclusion: Overexpression of CircMTO1 acts as tumor suppressor in liver cancer by sponging miR-9-5p, which upregulates NOX4.
Keywords: circMTO1, miR-9-5p/NOX4 axis, hepatocellular carcinoma, proliferation, apoptosis