110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

hsa_circ_0008285 通过靶向 miR-211-5p/SOX4 轴促进宫颈癌的进展
Authors Bai Y, Li X
Received 31 December 2019
Accepted for publication 26 April 2020
Published 26 May 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 3927—3936
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S244317
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Introduction: Emerging evidence has demonstrated that circRNAs are implicated in the progression of cervical cancer (CC). However, the roles and underlying mechanisms of circRNAs remain unclear in CC.
Methods: QRT-PCR was performed to detect hsa_circ_0008285 expression in CC tissues and cell lines. The roles of hsa_circ_0008285 on CC progression were explored by function assays. Next, the underlying mechanisms of hsa_circ_0008285 in CC progression were determined by bioinformatics analysis, dual-luciferase reporter and RIP assays.
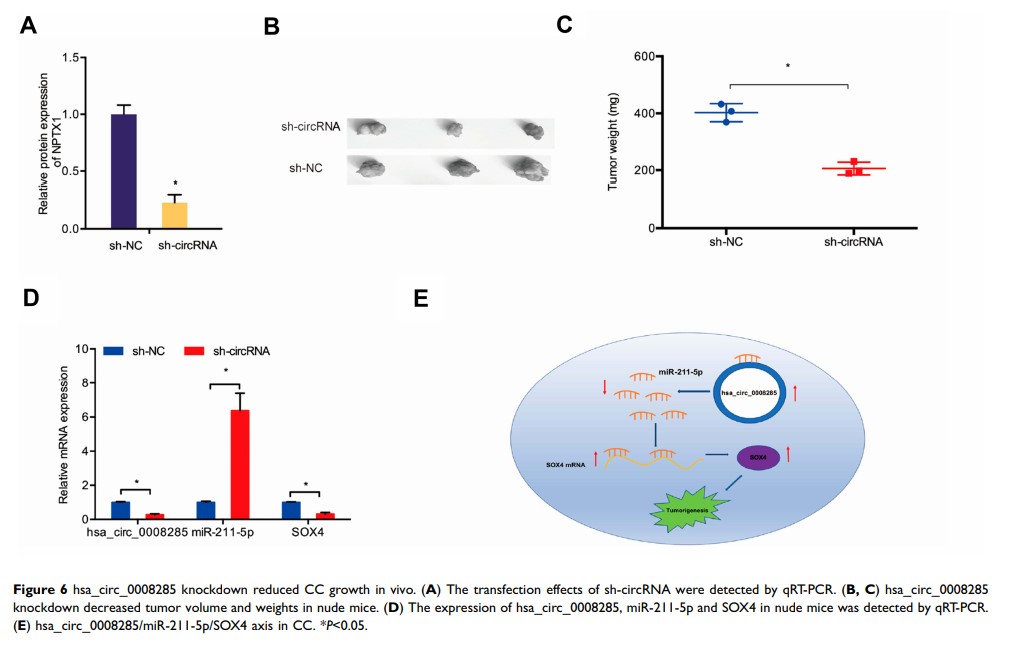
Results: In the present study, we identified a new circRNA hsa_circ_0008285, which was significantly up-regulated in CC tissues and cell lines. Loss-of-function assays showed that hsa_circ_0008285 suppression reduced the proliferation and invasion of CC cells in vitro and reduced tumor growth in vivo. In mechanism, bioinformatics analysis, dual-luciferase reporter and RIP assays showed that hsa_circ_0008285 served as a sponge for miR-211-5p in CC. Next, we confirmed that SOX4 served as a target gene for miR-211-5p in CC. Additionally, we revealed that miR-211-5p inhibitors abolished the effects of hsa_circ_0008285 on SOX4 expression in CC cells.
Conclusion: Therefore, our research highlighted that hsa_circ_0008285 promoted CC progression via serving as a ceRNA of miR-211-5p to release SOX4, which might provide a potential therapeutic target for tumor treatment.
Keywords: cervical cancer, hsa_circ_0008285, miR-211-5p, SOX4, ceRNA