110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在中国第三级教学医院分离的多重抗生素耐药的拟杆菌属 某些菌株的高发病率
Authors Wang Y, Han Y, Shen H, Lv Y, Zheng W, Wang J
Received 16 January 2020
Accepted for publication 16 May 2020
Published 27 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1537—1546
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S246318
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eric Nulens
Purpose: The study investigates the molecular epidemiology of multi-drug resistant (MDR) Bacteroides spp. isolates and the clinical characteristics of the patients.
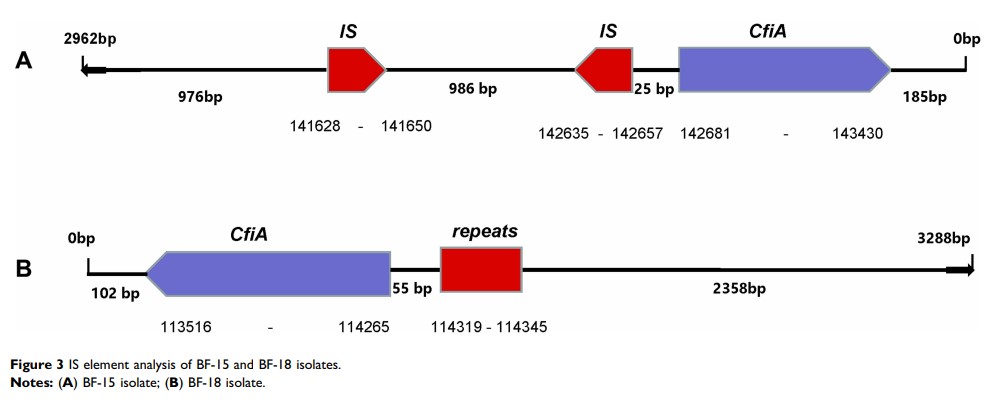
Materials and Methods: Bacteroides spp. clinical strains were identified through MALDI-TOF MS and VITEK-2 anaerobes and corynebacterium (ANC) cards. A broth microdilution method was employed to detect the antimicrobial sensitivities of Bacteroides spp. isolates. PCR was used to detect the resistance genes, including cfxA, cepA, cfiA, ermF, nim , as well as the upstream insertion sequence (IS) element of the cfiA gene. The effects of broad-spectrum efflux pump inhibitors (EPIs) on the minimal inhibitory concentration (MICs) of cefoxitin, moxifloxacin, and imipenem for MDR Bacteroides spp. were investigated.
Results: The total resistance rates of 115 Bacteroides spp. isolates to cefoxitin, moxifloxacin, clindamycin, metronidazole, imipenem and meropenem were 4.3%, 16.5%, 80.0%, 5.2%, 13.9% and 13.9%, respectively. The positive rates of carbapenem resistance gene cfiA were 38.9% and 8.6% for B. fragilis and non-B. fragilis isolates, respectively. The isolation rate of MDR isolates reached up to 18.26% (21/115), and the isolation rate among the gastrointestinal cancer patients was significantly higher when compared to the non-gastrointestinal cancer patients (52.38%/26.08%, P = 0.006). Furthermore, MDR isolates were more likely to be isolated from the patients exposed to cephalosporins 3 months before Bacteroides spp. isolation (76.19%/31.52%, P = 0.000).
Conclusion: The overall resistance rates of Bacteroides spp. isolates against multiple antimicrobials were at a high level, especially for B. fragilis . The CfiA gene carrying rate among B. fragilis isolates was as high as 38.9%, and its mediated carbapenem resistance was the major resistance mechanism for B. fragilis . The findings of this study imply that the real resistance tendency of Bacteroides spp. may be underestimated and need to be given more attention.
Keywords: anaerobe, Bacteroides fragilis , carbapenem resistance, clinical characteristics