110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

结合有 IFN-α2b 的光交联水凝胶,外加 T 细胞转移和低剂量照射用于治疗胃癌的优异抗肿瘤功效
Authors Liu Q, Zhang D, Qian H, Chu Y, Yang Y, Shao J, Xu Q, Liu B
Received 11 February 2020
Accepted for publication 7 May 2020
Published 27 May 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 3669—3680
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S249174
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
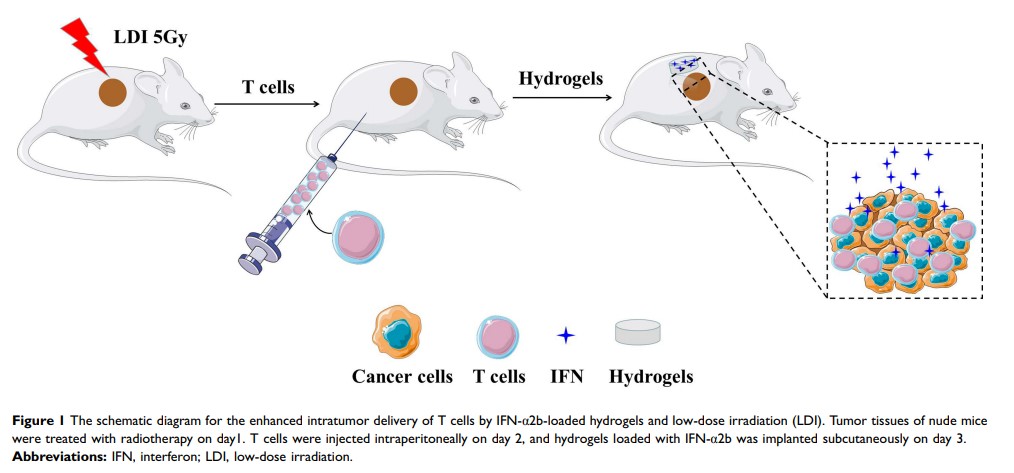
Introduction: The exhaustion and poor homing of activated lymphocytes are critical obstacles in adoptive cell immunotherapy for solid tumors. In order to effectively deliver immune cells into tumors, we encapsulated interferon-α 2b (IFN-α 2b) into macroporous hydrogels as an enhancement factor and utilized low-dose irradiation (LDI) as a tumoral attractor of T cells.
Methods: Hydroxypropyl cellulose hydrogels were prepared by irradiation techniques, and the cross-sectional microstructure was characterized by scanning electron microscopy. The synergistic antitumor mechanism of combination of IFN-α 2b and CIK cells was evaluated by detecting the expression of activation marker CD69 on CIK cell surface and IFN-γ production by CIK cells. The in vivo antitumor activity of IFN-α 2b-incorporated hydroxypropyl cellulose hydrogels combined with CIK and radiation was evaluated in an MKN-45 xenografted nude mice model.
Results: The bioactivity of IFN-α 2b was well maintained in ultraviolet-reactive, rapidly cross-linkable hydroxypropyl cellulose hydrogels. In vitro studies demonstrated IFN-α 2b-activated T cells, as evidenced by upregulating early activation marker CD69 and secretion inflammatory cytokine IFN-γ. In vivo real-time image showed our hydrogels kept a higher amount of drug delivery at the tumor site for a long time compared with free drug injection. Low-dose irradiation promoted T cell accumulation and infiltration in subcutaneous tumors. Combination of IFN-α 2b-loaded hydrogels (Gel-IFN) with T cells and LDI exhibited higher efficacy to eradicate human gastric cancer xenograted tumors with less proliferating cells and more necrotic regions compared with IFN-α 2b or T cells alone.
Discussion: HPC hydrogels kept the activity of IFN-α 2b and stably release of IFN-α 2b to stimulate T cells for a long time. At the same time, low-dose radiation recruits T cells into tumors. This innovative integration mode of IFN-α 2b-loaded hydrogels and radiotherapy offers a potent strategy to improve the therapeutic outcome of T cell therapy.
Keywords: gastric cancer, adoptive cell transfer, interferon-α 2b, hydrogels, low-dose irradiation