110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Six1 过表达通过调节 GLUT3、MMP2 和 Snail 促进甲状腺癌细胞的葡萄糖代谢和侵袭
Authors Yang C, Xu W, Gong J, Chai F, Cui D, Liu Z
Received 14 August 2019
Accepted for publication 28 April 2020
Published 29 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 4855—4863
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S227291
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Introduction: Sineoculis homeobox homolog 1 (Six1) overexpression has been implicated in several human cancers. To date, its clinical significance and potential function in human thyroid cancer remain unclear.
Methods: Immunohistochemistry was used to examine the protein expression of BCAT1 in 89 cases of thyroid cancer tissues. We overexpressed and knockdown Six1 in TPC-1 and B-CPAP thyroid cancer cell lines. Biological roles and potential mechanisms of Six1 were examined using CCK-8, colony formation assay, Matrigel invasion assay, Western blot, PCR, ATP assay, and 2-NBDG uptake assay.
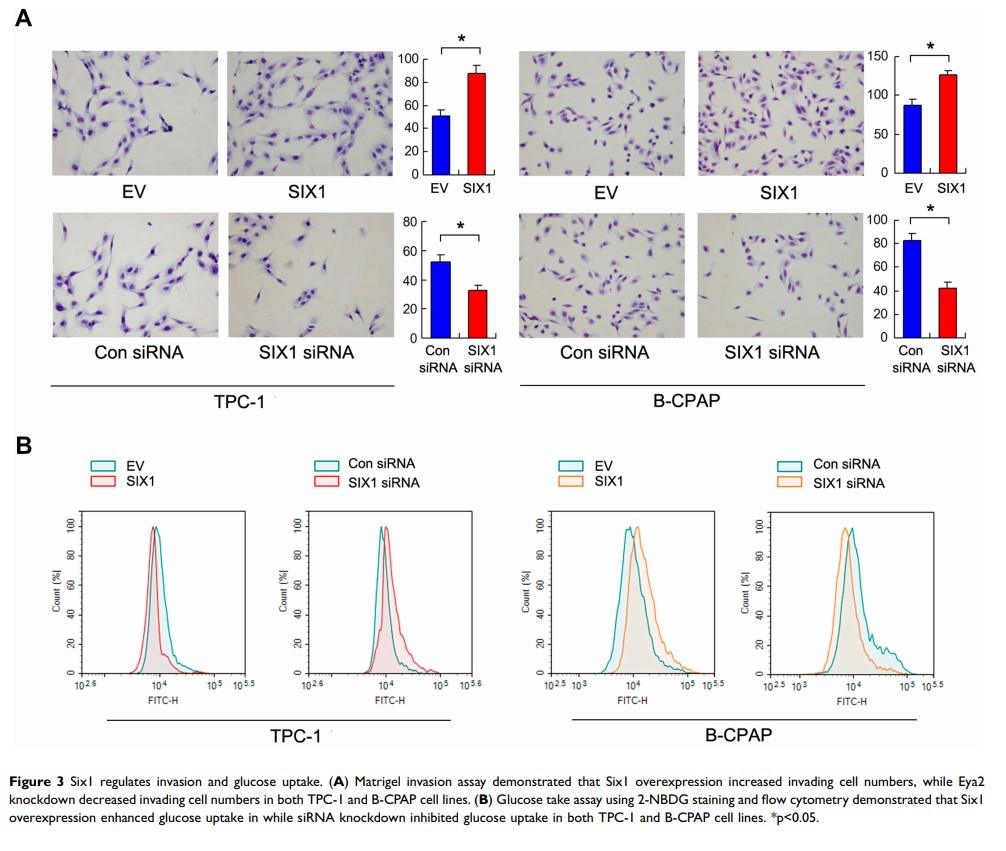
Results: We showed that Six1 protein was upregulated in thyroid cancers and was associated with tumor size and nodal metastasis. Analysis of TCGA dataset indicated that Six1 mRNA was higher in thyroid cancers compared with normal thyroid. CCK-8, colony formation and Matrigel invasion assays demonstrated that Six1 overexpression promoted proliferation, colony number and invasion while Six1 siRNA knockdown inhibited the growth rate, colony formation ability and invasive ability in both cell lines. Notably, Six1 upregulated glucose consumption, lactate production level and ATP level. 2-NBDG uptake analysis showed that Six1 overexpression upregulated glucose uptake while Six1 knockdown inhibited glucose uptake. Further analysis revealed that Six1 overexpression upregulated Snail, MMP2 and GLUT3 at both mRNA and protein levels. TCGA analysis demonstrated positive associations between Six1 and Snail, MMP2 and GLUT3 at the mRNA levels.
Conclusion: Taken together, our data demonstrated that Six1 was upregulated in human thyroid cancers and promoted cell proliferation and invasion. Our data also revealed new roles of Six1 in thyroid cancer development by modulating glucose metabolism and invasion, possibly through regulation of Snail, MMP2 and GLUT3.
Keywords: Six1, thyroid cancer, glucose metabolism, GLUT3