110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

羽扇豆醇可减轻与 PI3K/Akt 信号通路调控相关的脑缺血-再灌注损伤
Authors Wang Z, Han Y, Tian S, Bao J, Wang Y, Jiao J
Received 5 November 2019
Accepted for publication 8 April 2020
Published 2 June 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 1381—1390
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S237406
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yuping Ning
Background/Aim: This study aimed to investigate the effect and mechanism of lupeol on cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats.
Methods: The effects of lupeol on cerebral infarction, cerebral water content, neurological symptoms and cerebral blood flow in rats were evaluated. Nissl staining was carried out to assess the neuronal damage of ischemic brain after I/R in rats. Apoptosis of ischemic brain neurons after I/R was detected by TUNEL staining. Western blotting was carried out to detect the effects of lupeol on the expression of p-PDK1, p-Akt, pc-Raf, p-BAD, cleaved caspase-3 and p-PTEN.
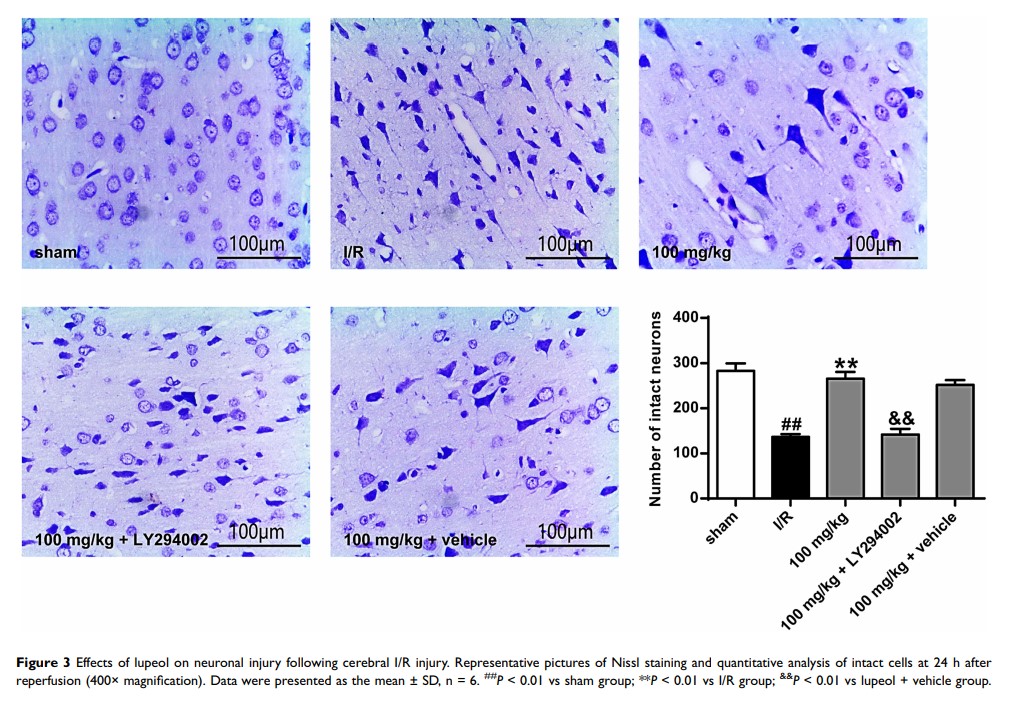
Results: Lupeol significantly increased cerebral blood flow after I/R in rats, reduced brain water content and infarct volume, and decreased neurological function scores. It significantly reduced neuronal damage after I/R in rats, and significantly reduced neuronal cell loss. PI3K inhibitor (LY294002) can eliminate the effect of lupeol on I/R in rats. In addition, lupeol significantly increased the protein expression of p-PDK1, p-Akt, pc-Raf, p-BAD, and down-regulated the expression of cleaved caspase-3. LY294002 reversed the effects of lupeol on the expression of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway-related proteins and cleaved caspase-3 after I/R in rats.
Conclusion: Lupeol had significant neuroprotective effects on brain I/R injury and neuronal apoptosis, and its mechanism may be related to the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Keywords: lupeol, PI3K/Akt, apoptosis, cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury