110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号传导途径调控长非编码 RNA 在非小细胞肺癌发病中的作用
Authors Lin S, Zhen Y, Guan Y, Yi H
Received 8 December 2019
Accepted for publication 26 April 2020
Published 3 June 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 4181—4191
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S241519
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
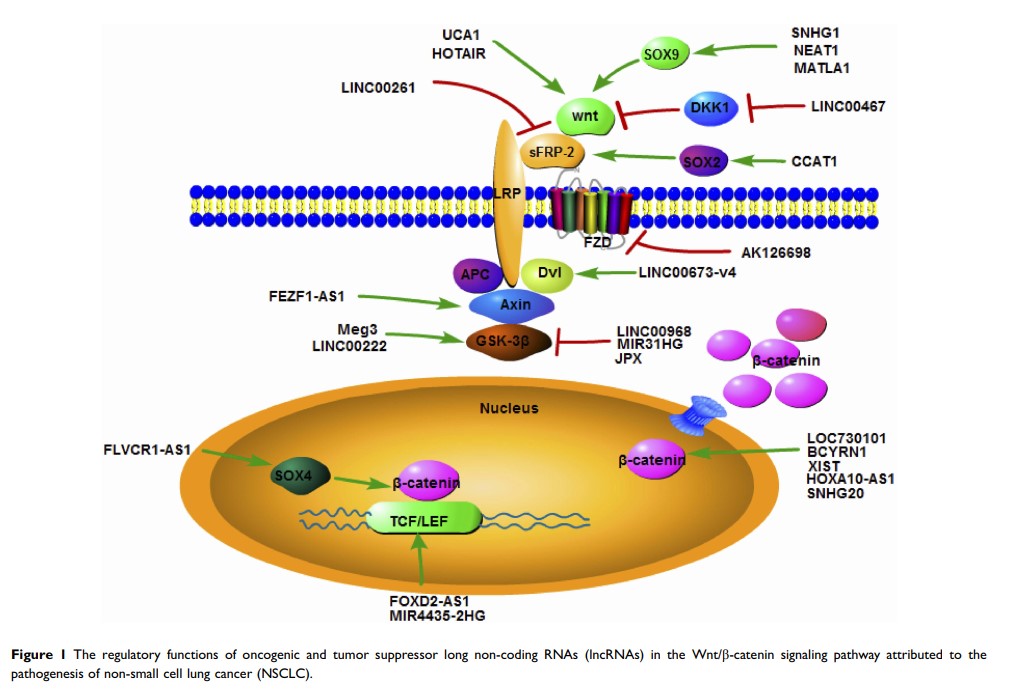
Abstract: Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common pathological type of lung cancer. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are promising novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, as well as potential therapeutic targets for lung cancer. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been demonstrated to modulate tumor cells proliferation, cell cycle progression, invasion, and metastasis by regulating gene expression at transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and epigenetic levels. The oncogenic aberrant Wnt/β-catenin signaling is prominent in lung cancer, playing a vital role in tumorigenesis, prognosis, and resistance to therapy. Interestingly, compelling studies have demonstrated that lncRNAs exert either oncogenic or tumor suppressor roles by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. In this review, we aim to present the current accumulated knowledge regarding the roles of Wnt/β-catenin signaling-regulated lncRNAs in the pathogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Better understanding of the effects of lncRNAs on Wnt/β-catenin signaling might contribute to the improved understanding of the molecular tumor pathogenesis and to the uncovering of novel therapeutic targets in NSCLC.
Keywords: long non-coding RNA, lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, pathogenesis, Wnt/β-catenin signaling