110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

硫化氢、脂肪组织和糖尿病
Authors Zhu L, Yang B, Ma D, Wang L, Duan W
Received 13 February 2020
Accepted for publication 9 May 2020
Published 3 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1873—1886
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S249605
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Ming-Hui Zou
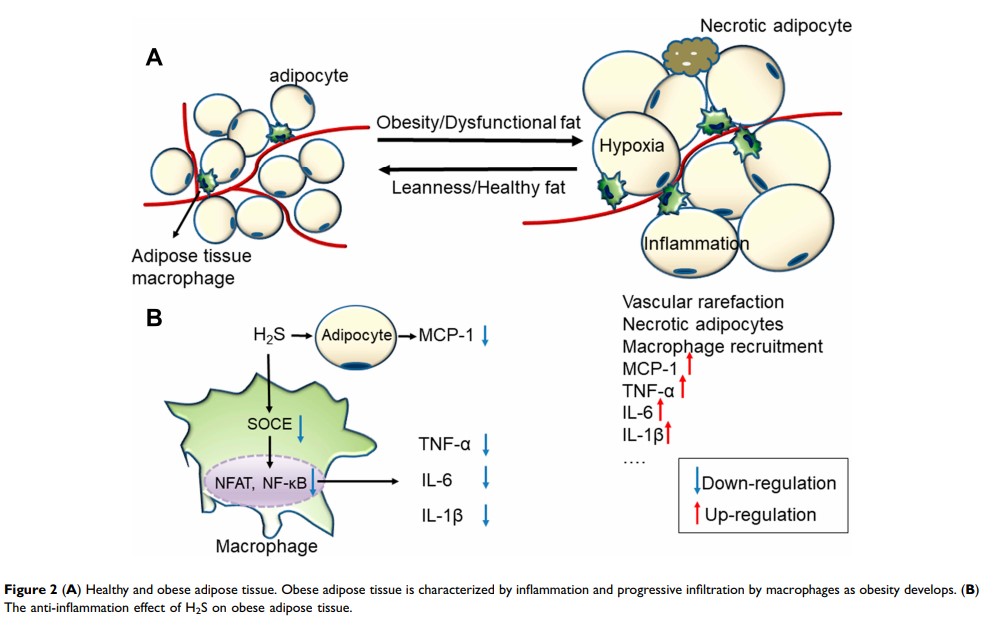
Abstract: Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is now increasingly considered to be the third gasotransmitter alongside other gaseous signaling molecules, nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide (CO). H2S is produced by a variety of endogenous enzymatic and non-enzymatic pathways and acts as a modulator of the physiological and pathological events of the body. Adipocytes express the cystathionine γ lyase (CSE)/H2S system, which modulates a variety of biological activities in adipose tissue (AT), including inflammation, apoptosis, insulin resistance, adipokine secretion and adipocyte differentiation. Abnormalities in the physiological functions of AT play an important role in the process of diabetes mellitus. Therefore, this review provides an overview of the general aspects of H2S biochemistry, the effect of H2S on AT function and diabetes mellitus and its molecular signalling mechanisms as well as the potential application of H2S in pharmacotherapy.
Keywords: hydrogen sulfide, adipose tissue, diabetes mellitus, drug therapy