110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

茉莉酸甲酯通过 Nrf2 依赖性 HO-1 信号通路保护小胶质细胞免受 β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的氧化应激和炎症
Authors Li H, Lv L, Wu C, Qi J, Shi B
Received 4 December 2019
Accepted for publication 31 March 2020
Published 4 June 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 1399—1410
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S241142
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yuping Ning
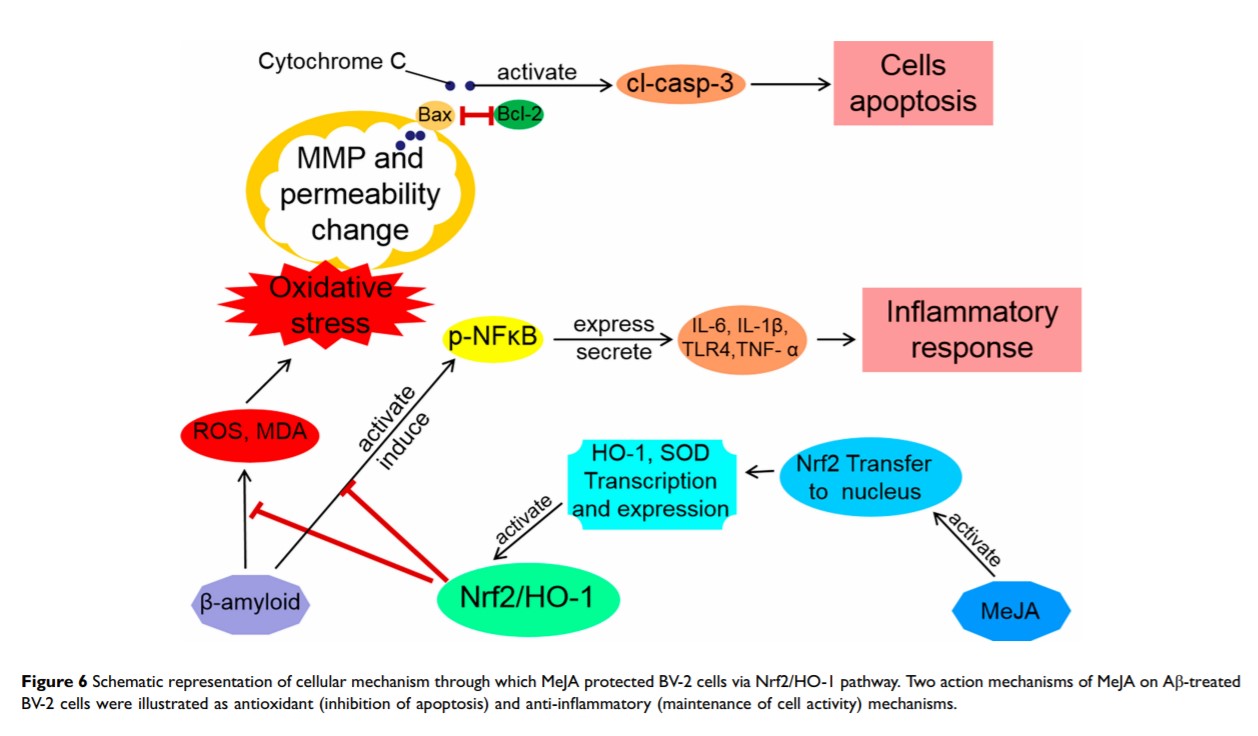
Background: β-Amyloid (Aβ) induces oxidative stress and inflammation of microglial cells, thus leading to Alzheimer’s disease. Methyl jasmonate (MeJA) is reported to have anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects. However, the potential roles of MeJA in Aβ-induced cell activities and the underlying mechanism are unclear.
Methods: Microglial cell line BV-2 was stimulated by 20 μM Aβ and/or 20 μM MeJA and then divided into four groups (control, Aβ, MeJA, and Aβ+MeJA). Cell viability was detected by MTT assay. MDA, SOD activity, and ROS were detected by fluorescence spectrophotometry and immunofluorescence assay. Nrf2 and HO-1 were detected by qRT-PCR and Western blot. Furthermore, inflammatory cytokines (p-NFκB, TLR4, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) and apoptosis factors (Bcl-2, Bax, and cl-casp-3) were detected by Western blot. TUNEL assay was applied to investigate apoptosis rate. Moreover, the mechanism of how MeJA played anti-oxidative stress and anti-inflammatory roles was investigated by silencing of Nrf2 via siRNA.
Results: The result of MTT assay showed that MeJA improved the decreased viability of BV-2 cells induced by Aβ. The detection of MDA, SOD activity, and ROS showed the oxidative stress levels were decreased in Aβ+MeJA group compared with Aβ group. Nrf2, HO-1, and SOD were significantly up-regulated in Aβ+MeJA group compared with Aβ group (p < 0.01). In contrast, inflammatory cytokines were significantly down-regulated in Aβ+MeJA group compared with Aβ group (p < 0.05). Similarly, the expressions of apoptosis cytokines and TUNEL assay suggested a decreased apoptosis rate in Aβ+MeJA group compared to Aβ group (p < 0.01). Finally, results of Nrf2 knockdown experiment showed down-regulations of anti-oxidative stress factors (Nrf2, HO-1 and SOD), up-regulations of inflammatory cytokines, and increased ratio of Bax to Bcl in Aβ+MeJA+si-Nrf2 group compared with Aβ+MeJA group (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: MeJA could relieve Aβ-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response in microglial cells by activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
Keywords: methyl jasmonate, Nrf2-dependent HO-1 pathway, β-amyloid, oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines