110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国 2 型糖尿病患者的动脉粥样硬化与糖尿病性视网膜病变之间的关联
Authors Zhang C, Wang S, Li M, Wu Y
Received 18 January 2020
Accepted for publication 12 May 2020
Published 8 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1911—1920
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S246497
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
Aim: To explore the association between the atherosclerosis and diabetic retinopathy (DR) in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: This hospital-based cross-sectional study included 949 patients (700 males and 249 females) with T2DM. The atherosclerotic parameters were assessed using the cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI), ankle-brachial index (ABI), and carotid plaque. DR was assessed and graded using digital retinal photography and fundus fluorescein angiography as either nonproliferative DR (NPDR) or proliferative DR (PDR). Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to identify the associations between the atherosclerotic parameters and DR status.
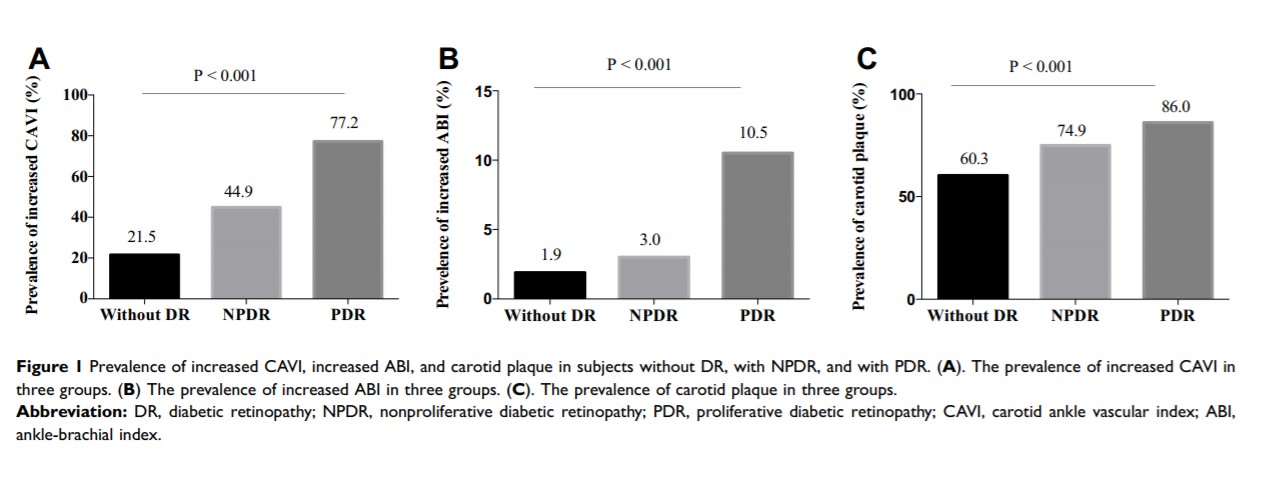
Results: The prevalence of DR was 23.6% in total patients, including 167 (17.6%) patients with NPDR and 57 (6.0%) patients with PDR. Patients with NPDR and PDR were more likely to have higher prevalence of increased CAVI, increased ABI, and carotid plaque than those without DR. In multivariable adjusted logistic regression analysis, patients with NPDR showed an odds ratio (OR) of 2.59 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.61– 4.19] for increased CAVI, 1.99 (0.62– 6.34) for increased ABI, and 1.75 (1.13– 2.71) for carotid plaque. Patients with PDR showed an OR of 7.83 (3.52– 17.41) for increased CAVI, 10.65 (3.33– 34.04) for increased ABI, and 11.40 (2.67– 48.63) for carotid plaque.
Conclusion: Both NPDR and PDR were independently associated with increased CAVI and presence of carotid plaque in Chinese patients with T2DM.
Keywords: atherosclerosis, cardio-ankle vascular index, diabetic retinopathy, ankle-brachial index, carotid plaque