110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

隐绿原酸通过在体内和体外抑制铁死亡对糖尿病中胰岛 β 细胞功能的保护作用
Authors Zhou Y
Received 11 February 2020
Accepted for publication 27 April 2020
Published 8 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1921—1931
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S249382
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
Purpose: Mulberry leaf extract has exerted better antidiabetic activities, while the effects of major active components in mulberry leaf extract are still unclear. Cryptochlorogenic acid (CCA) as the major active component in mulberry leaf extracts was investigated herein.
Materials and Methods: Rats were treated with 50mg/kg streptozotocin for the establishment of diabetic model in vivo, and cells were treated with 33.3 mM glucose for the establishment of cell model in vitro. HE staining assay was performed for observation of pancreatic pathology and aldehyde fuchsin staining assay for examining islet cell numbers. The iron content was detected via Perls staining assay with iron assay kit (ab83366). The malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH) and oxidized glutathione (GSSG) were detected by corresponding kits. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was performed for assessment of gene level and Western blot for measurement of protein expression level. The cell survival was detected via CCK-8 assay.
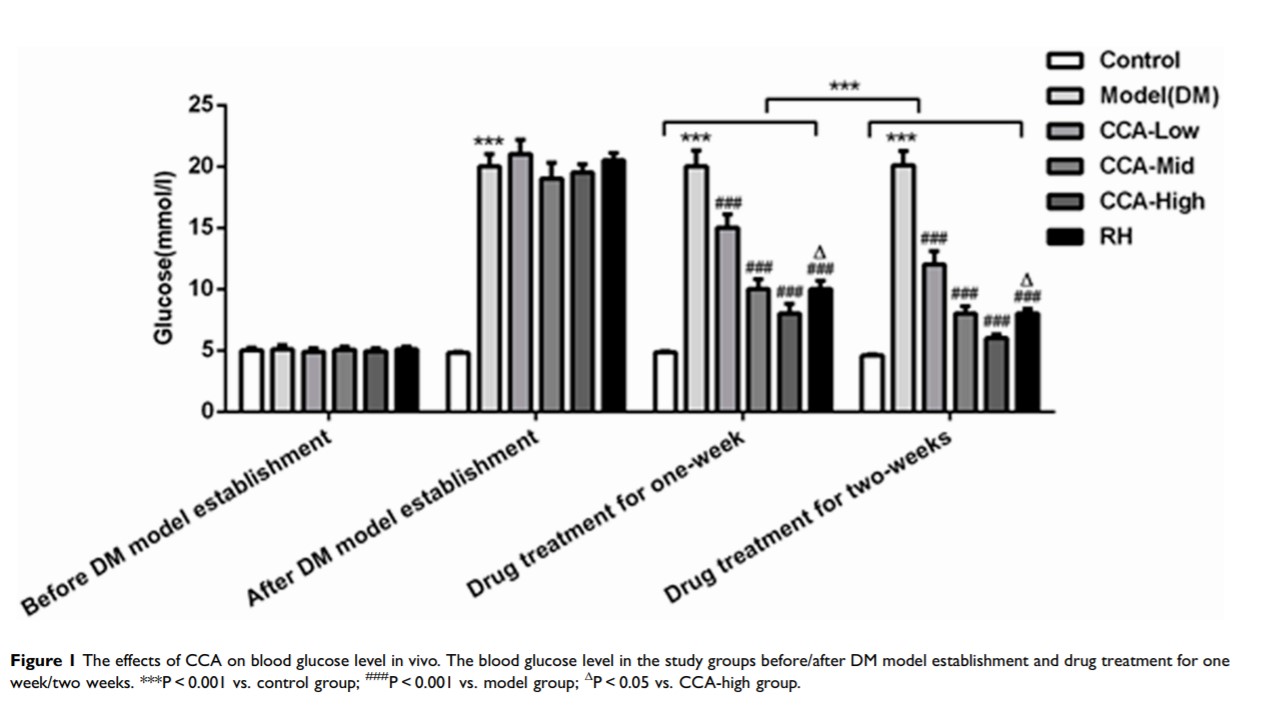
Results: The blood glucose level, iron content, accumulation of lipid peroxides and islet injury in diabetic model were all improved by CCA via a concentration-dependent manner. CCA functions via inhibition of ferroptosis by activation of cystine/glutamate transporter system (XC−)/glutathione peroxidase 4(GPX4)/Nrf2 and inhibition of nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4) in diabetes.
Conclusion: CCA exerted excellent antidiabetic effects via inhibition of ferroptosis, so it may be a promising agent for diabetes therapy, providing a new avenue for diabetes treatment.
Keywords: cryptochlorogenic acid, diabetes, XC-/GPX4, ferroptosis, Nrf2, NCOA4