110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

1,396 例胶质瘤患者 PD-1 基因表达、免疫特性和预后意义的综合分析
Authors Liu C, Zhang Z, Ping Y, Qin G, Zhang K, Maimela NR, Huang L, Yang S, Zhang Y
Received 11 November 2019
Accepted for publication 30 May 2020
Published 10 June 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 4399—4410
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S238174
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Background: Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) blockade therapy is one of the most remarkable immunotherapy strategies in many solid tumors, excluding glioma. The PD-1 expression, immune characteristics, and prognosis relevance in glioma remain poorly understood.
Patients and Methods: RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and mRNA microarray data were obtained for 325 and 301 glioma patients, respectively, from the Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas (CGGA) database. We analyzed the expression profile of PDCD1 (encoding PD-1) according to the different grade, isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation status, and molecular subtype of glioblastoma. Gene ontology (GO) analyses were performed to explore biological processes of PD-1-related genes. Survival analysis was conducted using the Kaplan–Meier method. The findings were validated using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) RNA-seq data from 697 glioma samples. We also confirmed the PDCD1 gene expression feature and survival relevance in our own cohort of 73 glioma patients. R language was used for statistical analysis and generating figures.
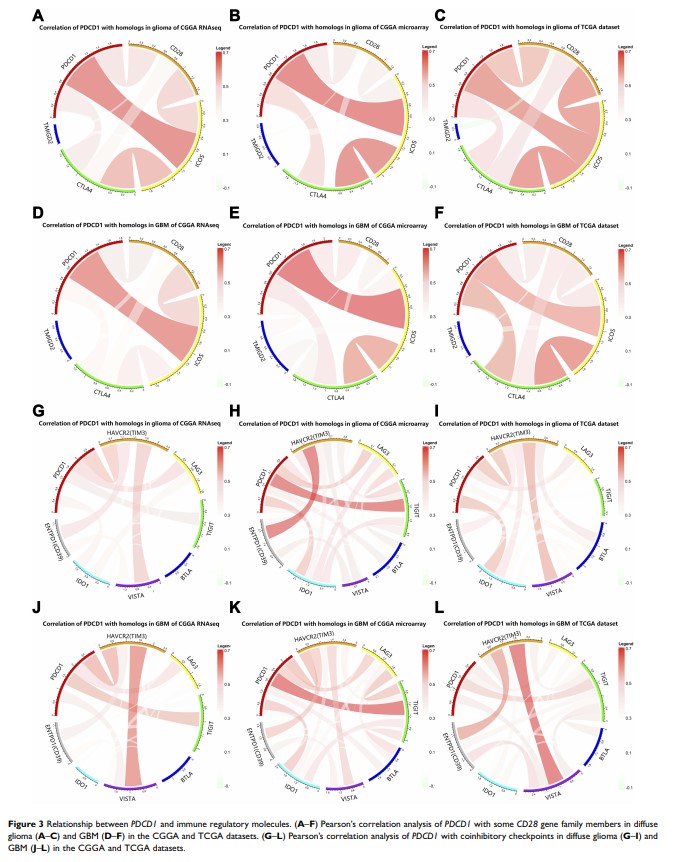
Results: PDCD1 was enriched in glioblastoma (WHO, grade IV), IDH wild-type glioma and mesenchymal glioblastoma in CGGA and TCGA datasets; similar results were validated in our own patient cohort. GO analysis revealed that PDCD1 -related genes were involved in inflammation immune responses and T cell-mediated immune responses in glioma. Circos plots indicated that PDCD1 was positively associated with CD28, ICOS , and the inhibitory checkpoint molecules CTLA4, HAVCR2, TIGIT , and LAG3 . Patients with PDCD1 upregulation had much shorter overall survival.
Conclusion: PDCD1 upregulation was found in more malignant phenotypes of glioma and indicated a worse prognosis. Immunotherapy of targeting PD-1 or combined with other checkpoint molecules (eg, TIM-3, LAG-3, or TIGIT) blockade may represent a promising treatment strategy for glioma.
Keywords: programmed cell death 1, glioma, The Cancer Genome Atlas, survival analysis, immunotherapy, costimulatory, inhibitory T-cell receptors