110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Erastin 对铁死亡的作用及其在癌症治疗中的前景
Authors Zhao Y, Li Y, Zhang R, Wang F, Wang T, Jiao Y
Received 22 March 2020
Accepted for publication 14 May 2020
Published 11 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 5429—5441
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S254995
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
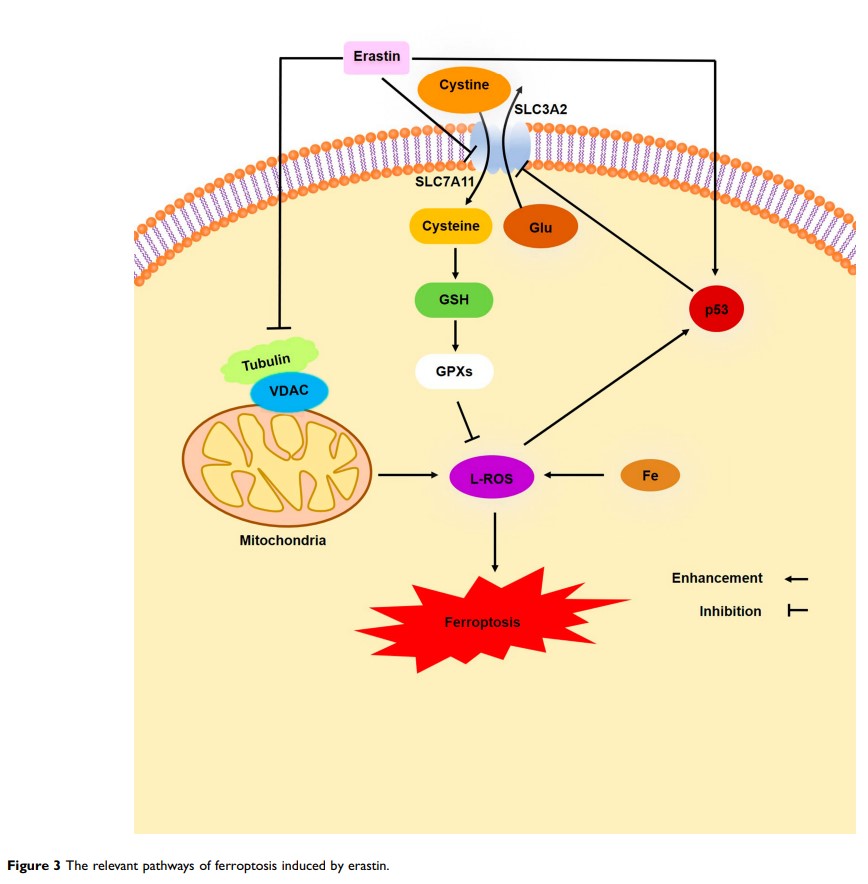
Abstract: Erastin was initially discovered as a small molecule compound that selectively kills tumor cells expressing ST and RASV12 and was later widely investigated as an inducer of ferroptosis. Ferroptosis is a recently discovered form of cell death caused by peroxidation induced by the accumulation of intracellular lipid reactive oxygen species (L-ROS) in an iron-dependent manner. Erastin can mediate ferroptosis through a variety of molecules including the cystine-glutamate transport receptor (system XC−), the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), and p53. Erastin is able to enhance the sensitivity of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, suggesting a promising future in cancer therapy. We hope that this review will help to better understand the role of erastin in ferroptosis and lay the foundation for further research and the development of erastin-based cancer therapies in the future.
Keywords: erastin, ferroptosis, system XC−, p53, VDAC, cancer