110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Wnt5a 的表达水平与第一代 EGFR-TKI 的治疗作用有关
Authors Zhang H, Yang X, Hu F, Li C, Xu J, Nie W, Shen Y, Lou Y, Han B, Zhong H, Zhang X
Received 16 February 2020
Accepted for publication 26 May 2020
Published 11 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 5387—5394
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S250024
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background and Objective: The first-generation epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) have shown significant therapeutic effects on patients harboring sensitive EGFR mutations, while the mechanisms related to drug resistance have still remained elusive. This study aimed to indicate the relationship between the expression level of Wnt5a with therapeutic effects of first-generation EGFR-TKIs on lung adenocarcinoma patients harboring sensitive EGFR mutations.
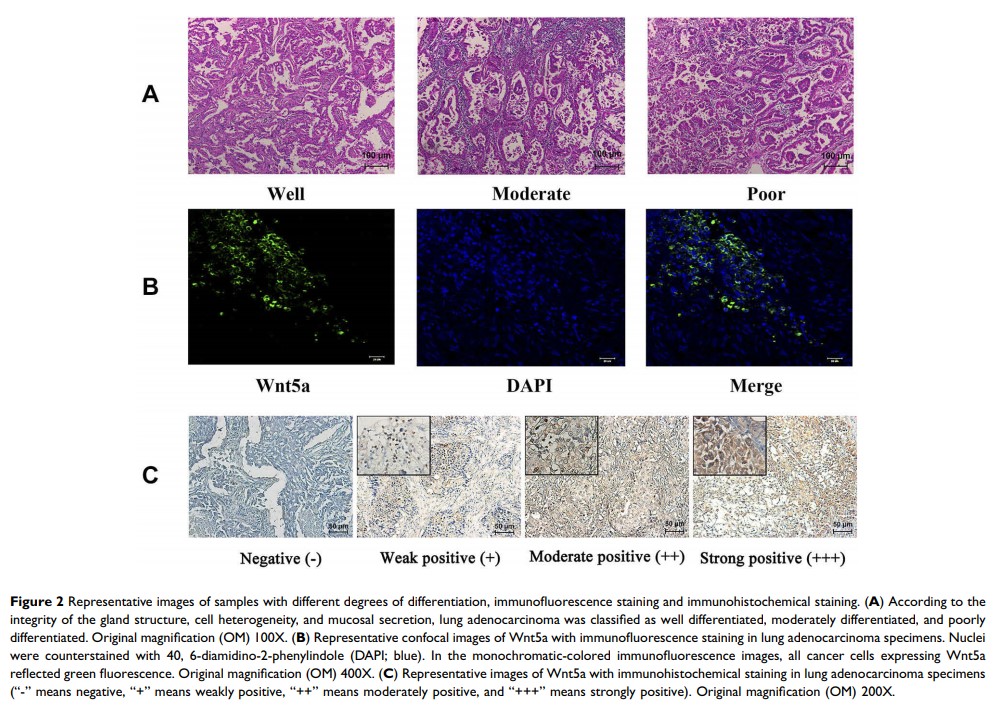
Methods: The medical records of 75 lung adenocarcinoma patients harboring sensitive EGFR mutations, who were admitted to our hospital and received first-generation EGFR-TKIs from June 1, 2010 to December 31, 2016, were analyzed. According to the efficacy of first-generation EGFR-TKIs, patients were divided into ineffective groups (progression-free survival (PFS) < 5 months) and effective groups (PFS > 26 months). Immunofluorescence staining, immunohistochemical staining and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) methods were utilized to detect the expression level of Wnt5a in the two groups.
Results: Among 75 patients, 36 patients were sensitive to first-generation EGFR-TKIs (effective group) and 39 patients were resistant to first-generation EGFR-TKIs (ineffective group). The location of Wnt5a was detected by immunofluorescence staining. Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated that the expression level of Wnt5a in the ineffective group was significantly higher than that in the effective group (P=0.0216). Besides, results of RT-PCR showed that the relative expression level of Wnt5a was remarkably higher in the ineffective group than that in the effective group (P=0.0135).
Conclusion: The expression level of Wnt5a was found to be associated with therapeutic effects of first-generation EGFR-TKIs in lung adenocarcinoma patients harboring sensitive EGFR mutations.
Keywords: tyrosine-kinase inhibitors, Wnt5a, epidermal growth factor receptor mutation, therapeutic effect