110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

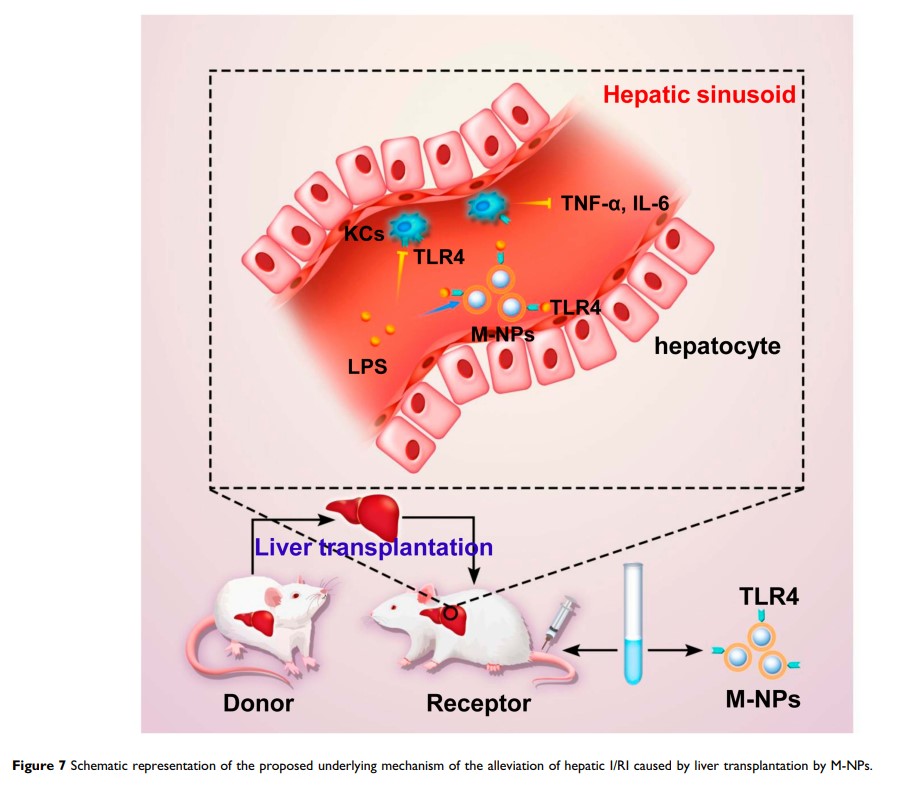
巨噬细胞膜包覆的纳米颗粒通过中和内毒素可减轻由原位肝移植引起的肝脏缺血再灌注损伤
Authors Ou Z, Zhong H, Zhang L, Deng M, Zhang W, Wang J, Feng H, Gong J, Miao C, Yi Z
Received 9 March 2020
Accepted for publication 19 May 2020
Published 11 June 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 4125—4138
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S253125
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Purpose: To investigate the effect and mechanism of macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticles (M-NPs) on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (I/RI) caused by orthotopic liver transplantation. In addition, the advantages of TLR4+/M-NPs compared to M-NPs are discussed.
Materials and Methods: We prepared biomimetic M-NPs and identified their characteristics. M-NPs were injected into an SD rat model of orthotopic liver transplantation, and the anti-inflammatory and anti-I/RI activities of M-NPs were studied in vivo and in vitro. In addition, we overexpressed macrophage membrane Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in vitro and prepared TLR4+/M-NPs. Then, we assessed the characteristics and advantages of TLR4+/M-NPs.
Results: The M-NPs neutralized endotoxin, inhibited the overactivation of Kupffer cells (KCs) and suppressed the secretion of inflammatory factors by inhibiting the endotoxin-mediated TLR4/MyD88/IRAK1/NF-κB signaling pathway. In an orthotopic liver transplantation model in SD rats, M-NPs showed significant therapeutic efficacy by neutralizing endotoxin and suppressing the secretion of inflammatory factors. Moreover, overexpression of TLR4 on the macrophage membrane by using a TLR4+-plasmid in vitro effectively reduced the amount of M-NPs needed to neutralize an equivalent dose of endotoxin, reducing the potential risks of NP overuse.
Conclusion: This study indicates that M-NPs can effectively alleviate I/RI induced by liver transplantation.
Keywords: biomimetic nanoparticle, endotoxin, Kupffer cell, liver transplantation, ischemia reperfusion injury