110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

金银花 Carbonisata 衍生的碳点对脂多糖诱导的发热和体温过低大鼠模型的功效
Authors Wu J, Zhang M, Cheng J, Zhang Y, Luo J, Liu Y, Kong H, Qu H, Zhao Y
Received 5 February 2020
Accepted for publication 25 May 2020
Published 12 June 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 4139—4149
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S248467
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Introduction: A correlation is established between the efficacy of Chinese herbal medicine and its charcoal drugs. Lonicerae japonicae Flos (LJF) is commonly used to treat fever, carbuncle, and tumors, among others. LJF Carbonisatas (LJFC) is preferred for detoxifying and relieving dysentery and its related symptoms. However, the mechanisms underlying the effects of LJFC remain unknown.
Aim: The aim of this study was to explore the effects of LJFC-derived carbon dots (LJFC-CDs) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced fever and hypothermia rat models.
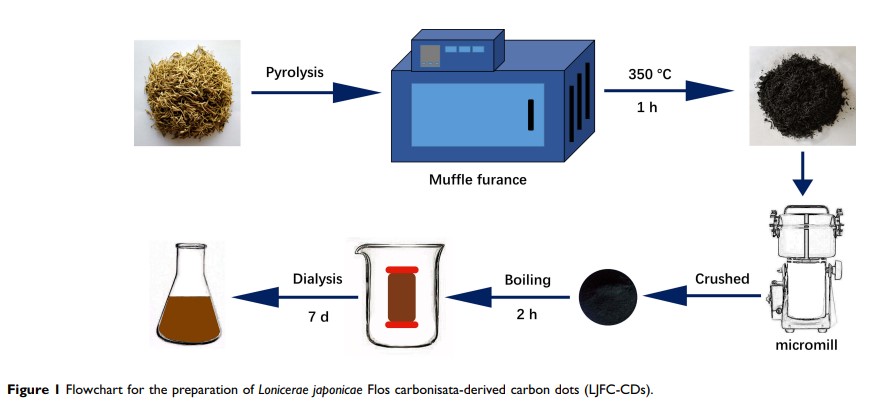
Methods: LJFC-CDs were characterized using transmission electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, Fourier-transform infrared, ultraviolet, fluorescence, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. The anti-inflammatory effects of LJFC-CDs were evaluated and confirmed using rat models of LPS-induced fever or hypothermia.
Results: The LJFC-CDs ranged from 1.0 to 10.0 nm in diameter, with a yield of 0.5%. LJFC-CDs alleviated LPS-induced inflammation, as demonstrated by the expression of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6 and the recovery of normal body temperature.
Conclusion: LJFC-CDs may have an anti-inflammatory effect and a potential to alleviate fever and hypothermia caused by inflammation.
Keywords: carbon dots, Lonicerae japonicae Flos, anti-inflammatory, lipopolysaccharide