110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:细胞分化剂 2(CDA-2)通过 miR-124/MAPK1 抑制 Saos-2 细胞的生长和迁移
Authors Li Q, Li G, Liu C, Chen N, Deng B, Xie Y
Received 8 February 2020
Accepted for publication 15 May 2020
Published 15 June 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 4541—4548
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S248851
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
***本文章已被撤回***
Background: CDA-2 (cell differentiation agent 2), isolated from healthy human urine, exerts antitumor effects in multiple types of cancer cells. However, its role in osteosarcoma has not been studied.
Methods: The MTT assay was used to examine the cell proliferation rate. A colony formation assay was used to examine cell growth. The Transwell assay was used to examine cell migration ability. A real-time PCR assay was used to examine the expression levels of miR-124 and MAPK1. A Western blot assay was used to examine protein expression levels. MAPK1 was selected as a possible target of miR-124, and the targeting relationship was examined by a luciferase reporter assay.
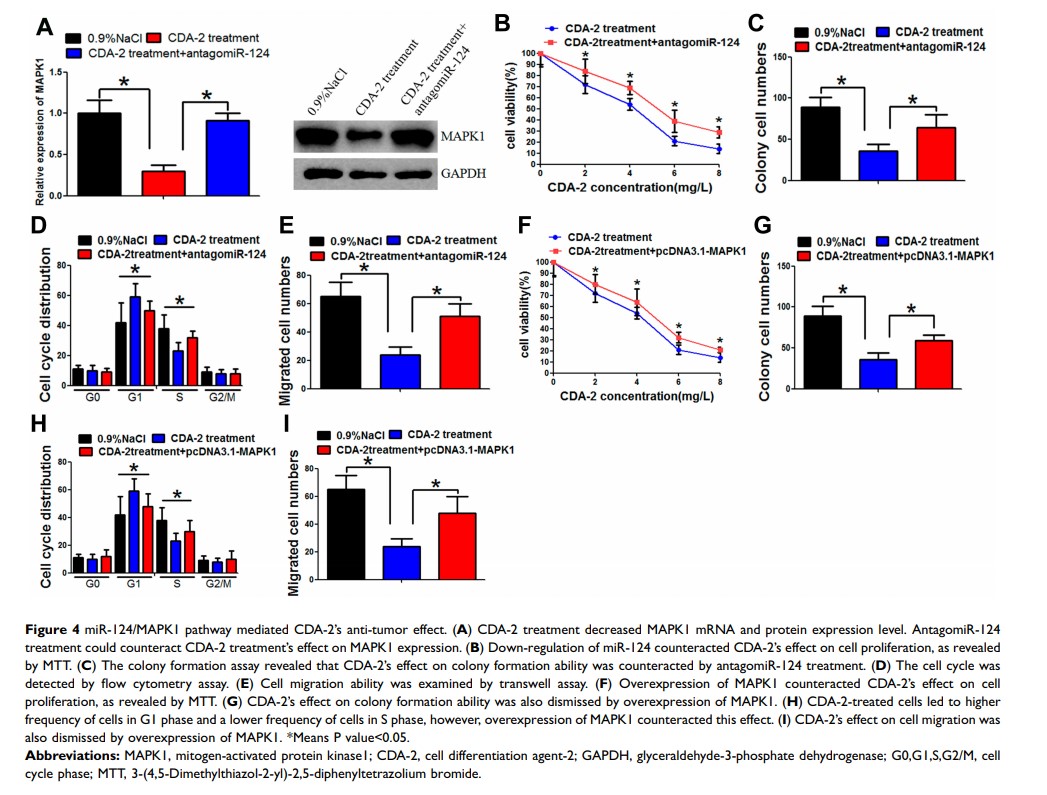
Results: We revealed that CDA-2 decreased the growth, migration and invasion ability of the osteosarcoma cell line Saos-2. Further study revealed that CDA-2 elevated the expression level of miR-124. MAPK1 was identified as a downstream target of miR-124. Knockdown of miR-124 or overexpression of MAPK1 counteracted CDA-2’s effects on cell growth and invasion.
Conclusion: Our data revealed that the miR-124/MAPK1 axis mediated CDA-2’s function in Saos-2 cells. CDA-2 can be used as a new treatment strategy for osteosarcoma.
Keywords: cell differentiation agent 2, osteosarcoma, miR-124, MAPK1