110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

细胞因子的基因多态性可影响术后镇痛药物舒芬太尼的剂量及效果
Authors Guo J, Yuan F, Yang Y, Li Y, Bao F, Guo X, Feng Z
Received 17 February 2020
Accepted for publication 6 May 2020
Published 16 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1461—1470
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S250174
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Robert B. Raffa
Objective: To explore the effect of genetic polymorphisms of cytokines on the dosage of sufentanil for patient-controlled intravenous analgesia (PCIA) after radical lung cancer surgery.
Methods: A total of 100 patients, aged 18 years and above, with ASA grade Ⅰ-Ⅱ and body mass index (BMI) 18.5 to 30, and who were scheduled for radical lung cancer surgery under total intravenous anaesthesia with PCIA of sufentanil from September 2015 to March 2016, were selected. DNA was collected from peripheral blood samples before surgery, and the iMLDRTM multiple single-nucleotide polymorphism typing kit was used to detect 16 related single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites of interleukin-1A (IL-1A), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-1RN (IL-1RN), interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8 (CXCL8), interleukin-10 (IL-10), tumour necrosis factor (TNF), nuclear factor kappa-B1 (NFκB1), REL (REL proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit), and nuclear factor kappa-B inhibitor alpha (NFκBIA). The general characteristics of patients, surgery and anaesthesia data, postoperative resting VAS pain scores, postoperative opioid dosages of sufentanil for PCIA and opioid-related adverse events were recorded. The effects of the examined genetic polymorphisms of the cytokines on the dosage of sufentanil were analysed.
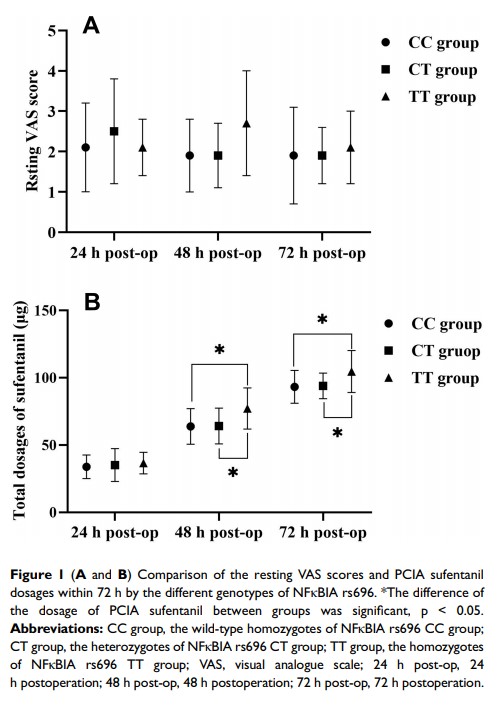
Results: Eight of 100 patients withdrew for various reasons, and, eventually, 92 patients were included. The patients’ resting visual analogue scale (VAS) scores at 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h after surgery were 2.3 ± 1.2, 2.0 ± 0.9, and 1.9 ± 1.0, respectively. The total amounts of sufentanil used were 34.7 ± 10.5 μg, 65.2 ± 13.7 μg, and 94.7 ± 11.6 μg, respectively. We found that the TT genotype of NFκBIA rs696 had higher PCIA sufentanil dosages than the CC genotype and the CT genotype at 48– 72 h postoperation (p=0.023, p=0.025, respectively).
Conclusion: The genetic polymorphisms of the cytokine NFκBIA rs696 might affect the dosage of sufentanil for PCIA after radical lung cancer surgery. The specific mechanism needs further study.
Keywords: genetic polymorphisms, single-nucleotide polymorphism, SNP, patient-controlled intravenous analgesia, PCIA, nuclear factor kappa-B inhibitor alpha, NFκBIA