110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国妊娠中两种甘油三酸酯相关指标对妊娠糖尿病的预测能力和大于胎龄儿现象:一项初步队列研究
Authors Liu PJ, Liu Y, Ma L, Yao AM, Chen XY, Hou YX, Wu LP, Xia LY
Received 28 February 2020
Accepted for publication 27 May 2020
Published 16 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2025—2035
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S251846
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Juei-Tang Cheng
Background/Aims: To investigate the potential of maternal first-trimester triglyceride (TG) to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-c) ratio, triglyceride glucose index (TyG) and total cholesterol (TC)/HDL-c to predict the risk of later gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and large for gestational age (LGA) newborn in Chinese women.
Methods: We included 352 women with a singleton pregnancy, who were followed up prospectively from the first prenatal visit until delivery. Fasting glucose and plasma lipid profiles including TG, TC, HDL-c, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) were measured in the first trimester. A binary logistic regression analysis was performed to determine the odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of GDM and LGA according to tertiles of those indices, respectively. Receiver-operating characteristic curve (ROC) and areas under the curve (AUC) were employed to evaluate the ability of those indices to predict the risk of GDM and LGA infants, and differences in the AUC values between them were compared.
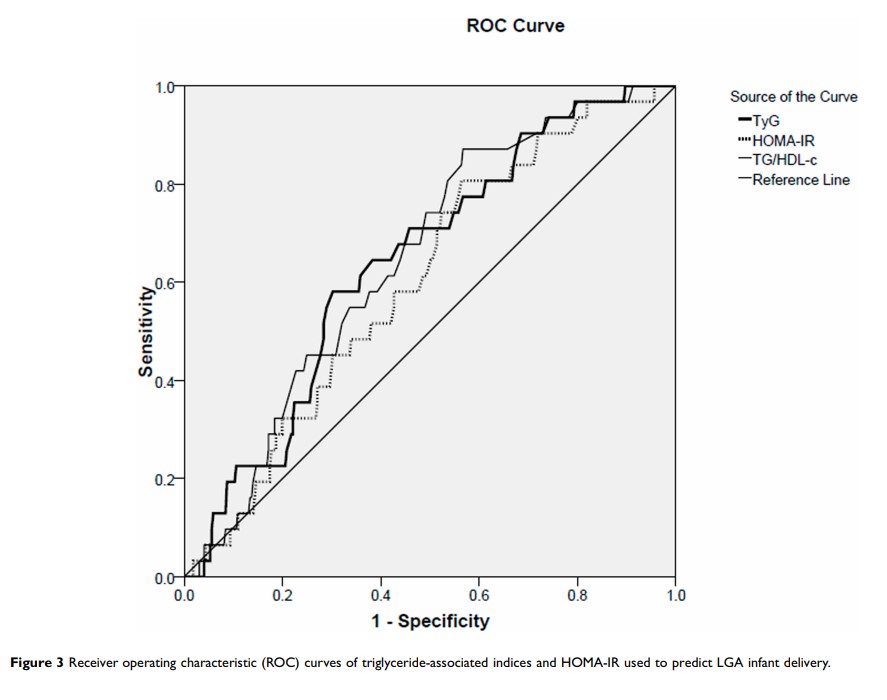
Results: Women with the top tertile of TG/HDL-c or TyG other than TC/HDL-c had a significantly higher risk of GDM (ORTG/HDL-c=2.388, 95% CI 1.026– 5.467; ORTyG=3.535, 95% CI 1.483– 8.426, respectively) and LGA infant delivery (ORTG/HDL-c=3.742, 95% CI 1.114– 12.569; ORTyG=3.011, 95% CI 1.012– 8.962, respectively) than women with the lowest tertile of TG/HDL-c or TyG after adjusting for confounders. The AUC of TG/HDL-c and TyG to detect GDM was 0.664 (95% CI 0.595– 0.733) and 0.686 (95% CI 0.615– 0.756), respectively, and that to detect LGA was 0.646 (95% CI 0.559– 0.734) and 0.643 (95% CI 0.552– 0.735), respectively (all P < 0.01). There were no statistical differences between TG/HDL-c and TyG in the ability of predicting the risk of GDM or LGA infants.
Conclusion: Maternal first-trimester TG/HDL-c and TyG are both good indicators in predicting the risk of later GDM and LGA newborn, and it may be useful to evaluate them in early pregnancy.
Keywords: gestational diabetes, triglyceride/HDL-c ratio, triglyceride glucose index, large for gestational age infant