108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

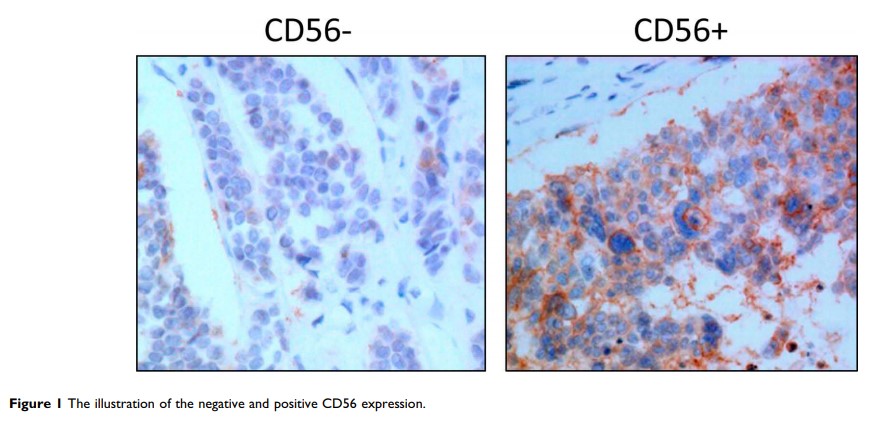
CD56 表达与胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤的生物学行为有关
Authors Chen X, Guo C, Cui W, Sun K, Wang Z, Chen X
Received 16 February 2020
Accepted for publication 20 May 2020
Published 17 June 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 4625—4631
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S250071
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Purpose: CD56 is a neural cell adhesion molecule that plays a role in the cohesiveness of neuroendocrine cells. The aim of this study was to explore the biological values of CD56 expression in pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (PNENs) and its role in predicting PNENs grades.
Patients and Methods: A total of 138 patients with histological-proven PNENs was included (66 G1, 46 G2 and 26 G3). The clinicopathological characteristics, including mitosis count, ki67 index, chromogranin A (CgA), synaptophysin (Syn) and CD56 expression, were evaluated. We assessed the diagnostic performance of markers in predicting PNEN G3 and the association between CD56 expression and risk of G3 or organs invasion.
Results: Lack of CD56 immunoreaction (CD56-) was more common in PNEN G3 than G1/G2 (31% vs 0– 2%, p < 0.01). The sizes of CD56- tumors were larger than CD56 positive tumors in PNEN G3 (p < 0.01). The odds ratio (OR) of CD56- expression was 13.6 [95% confidence interval (CI): 2.1– 88.1] in predicting PNEN G3. The OR of CD56- expression was 6.5 (95% CI: 1.1– 38.6) and 31.9 (95% CI: 1.09– 938.3) in predicting organs invasion and neuroendocrine carcinoma in PNEN G3, respectively. Tumor size (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.77 and size+CD56- expression [AUC = 0.84]) had acceptable performance in predicating PNEN G3.
Conclusion: Lack of CD56 immunoreaction may be a predictor and biological behavior marker for PNEN G3.
Keywords: pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm, grade, pancreatic neuroendocrine carcinoma, CD56