110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

YAP1 促进有乙型肝炎病毒感染的鼻咽癌的肿瘤侵袭和转移
Authors Huang Z, Su B, Liu F, Zhang N, Ye Y, Zhang Y, Zhen Z, Liang S, Liang S, Chen L, Luo W, Claret FX, Huang Y, Xu T
Received 30 January 2020
Accepted for publication 11 May 2020
Published 17 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 5629—5642
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S247699
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
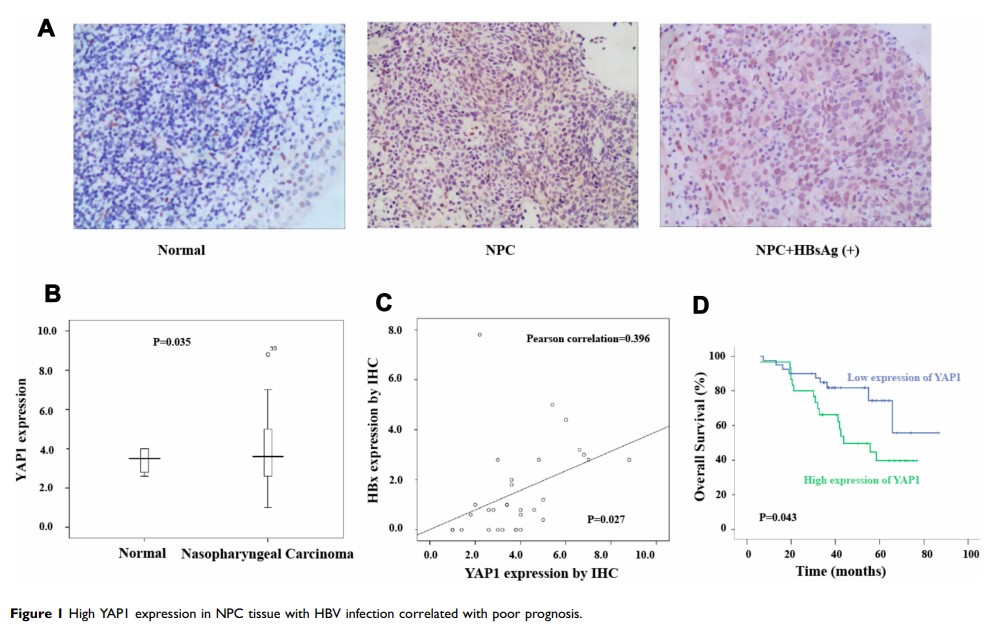
Introduction: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients with HBsAg (+) commonly present with high frequencies of distant metastasis and poor survival rate; however, the mechanism has not been elucidated.
Materials and Methods: We analyzed the yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) expression between HBsAg (+) and HBsAg (-) of NPC patients, then analyzed the relationship of YAP1 with survival. We further explored the anti-tumor role in NPC cell lines using YAP1 siRNA technique, and checked whether YAP1 regulatesepithelial–mesenchymal transition ( EMT). The relationship between HBV X protein (HBx) and YAP1 was also tested using Dual-Luciferase reporter assay. Finally, we explored anti-YAP1 to inhibit tumor metastasis using the xenograft mice model.
Results: In the current study, we found that YAP1 expression was higher in HBsAg (+) samples than in the HBsAg (-) samples, as a clinical signature, suggesting that YAP1 could be used as a prognostic factor for NPC. Our results showed that the HBx could regulate YAP1, further promoting cellular invasiveness through EMT. Anti-YAP1 can also decrease metastasis in vivo.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that YAP1 is a promising prognostic factor in NPC and could be used as a potential treatment target for NPC with HBV infection.
Keywords: YAP1, hepatitis B, HBx, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, metastasis