110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

二甲双胍通过在体内和体外调节 p53 和 RAP2A 来减少 1 型糖尿病的胰岛素抵抗
Authors Ren GF, Xiao LL, Ma XJ, Yan YS, Jiao PF
Received 13 February 2020
Accepted for publication 7 May 2020
Published 17 June 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 2381—2392
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S249557
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Purpose: Patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D) are associated with a high risk of multiple complications, so the development of T1D treatment is urgently needed. This study was set out to explore the molecular mechanism of metformin in the treatment of T1D insulin resistance.
Patients and Methods: Subcutaneous adipose tissues were collected from 68 T1D patients and 51 healthy controls. Insulin resistance model rats and cells were constructed and treated with metformin respectively. Western blot was used to detect p53 and RAP2A protein levels, and qPCR was utilized to measure p53 and RAP2A mRNA levels. SiRNA and RAP2A siRNA vectors were constructed to observe their effects on insulin resistance model cells.
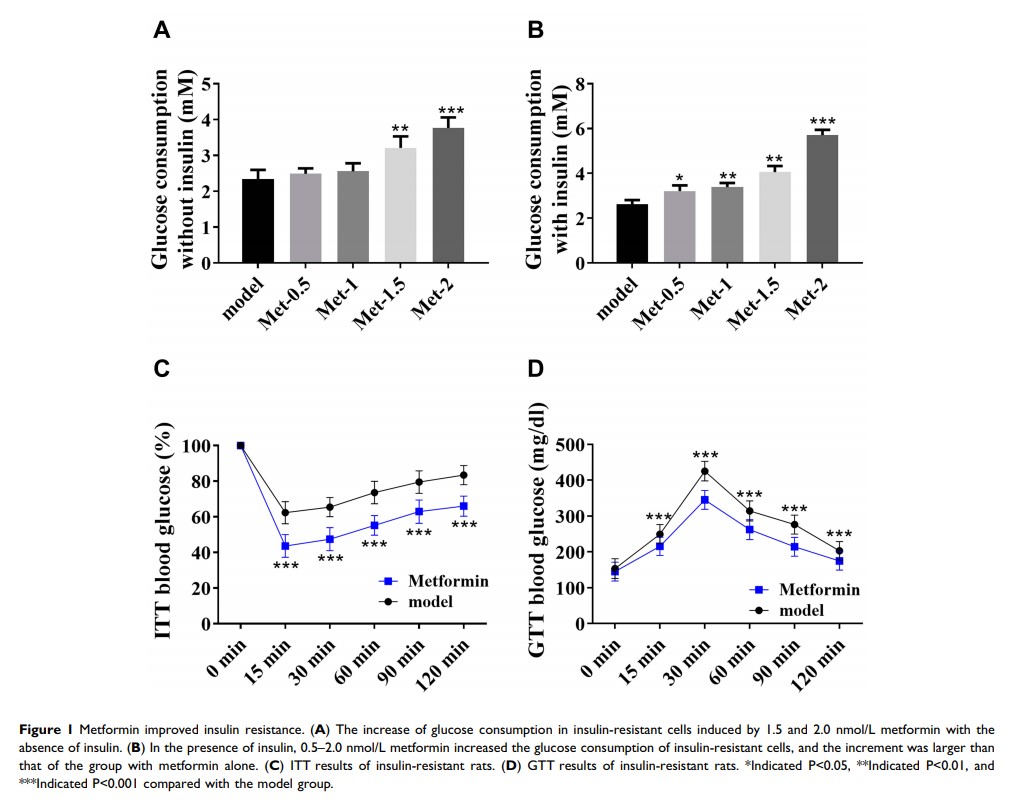
Results: In T1D, p53 was up-regulated, while RAP2A was down-regulated. Metformin could effectively improve insulin resistance and inflammatory response while down-regulating p53 and up-regulating RAP2A. P53 induced insulin resistance and inflammatory response by inhibiting RAP2A and promoted apoptosis.
Conclusion: Metformin improves T1D insulin resistance and inflammatory response through p53/RAP2A pathway, and the regulation of p53/RAP2A pathway is conducive to improving the efficacy of metformin in the treatment of insulin resistance.
Keywords: type 1 diabetes, p53, RAP2A, insulin resistance, metformin