110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

福建酸竹提取物通过硫氧还蛋白 1 的正向调节,在体外减轻紫外线诱导的皮肤细胞损伤
Authors Huang J, Xu Q, Lin M, Cheng B, Ji C
Received 25 November 2019
Accepted for publication 29 May 2020
Published 17 June 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 897—905
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S239920
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Introduction: Skin, as the outermost organ, is exposed to a wide range of environmental risk factors including ultraviolet (UV) and all kinds of pollutants. Excessive UV exposure contributes to many disorders, such as photoaging, skin inflammation, and carcinogenesis.
Methods: To determine the effects of bamboo extract (BEX) from our local plant, Acidosasa longiligula , on UV-irritated human skin, we conducted a variety of studies, including Western blot, apoptosis assays, reactive oxygen species (ROS) detection, and thioredoxin (TXN) and thioredoxin reductase (TXNRD) activity assays in primary skin keratinocytes.
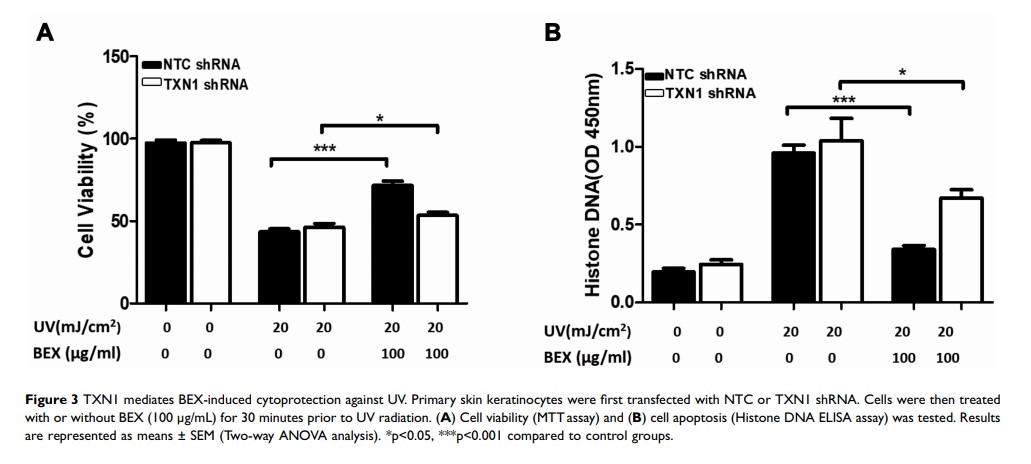
Results: We first determined that BEX protects human skin keratinocytes against UV radiation-induced apoptosis and ROS production. UV radiation can robustly impair TXN and TXNRD activity which can, in turn, be significantly rescued by BEX treatment. Moreover, BEX regulates TXN1 levels in primary skin keratinocytes and TXN1 is proved to be required for the protective function of BEX. Last, we found that the NF-κB/p65 pathway mediates the protective function of BEX against UV.
Discussion: Collectively, our work delineates the beneficial role of BEX in UV-induced skin cell damage and provides a novel therapeutic reagent to prevent or alleviate the progress of photoaging and other UV-provoked skin diseases.
Keywords: Acidosasa longiligula , bamboo extract, BEX, ultraviolet radiation, UV radiation, thioredoxin, TXN, NF-κB pathway