110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

RARβ 基因 DNA 甲基化作为健康生活方式与乳腺癌之间关联的介质:一项病例对照研究
Authors Wang X, Liu Y, Sun H, Ge A, Li D, Fu J, Li Y, Pang D, Zhao Y
Received 3 January 2020
Accepted for publication 20 May 2020
Published 18 June 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 4677—4684
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S244606
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Xueqiong Zhu
Purpose: Lifestyle factors and methylation in the retinoic acid receptor β (RARβ ) gene are associated with breast cancer (BC). This study aims to examine the mediation effect of RARβ methylation on the association between healthy lifestyle and BC in Chinese women.
Patients and Methods: This case–control study consisted of 408 BC patients and 573 controls. A healthy lifestyle score (HLS) was constructed based on diet, alcohol use, physical activity, body mass index and smoking. The mediation effect of RARβ methylation in peripheral blood leukocytes was assessed in a causal mediation model using R package Lavaan.
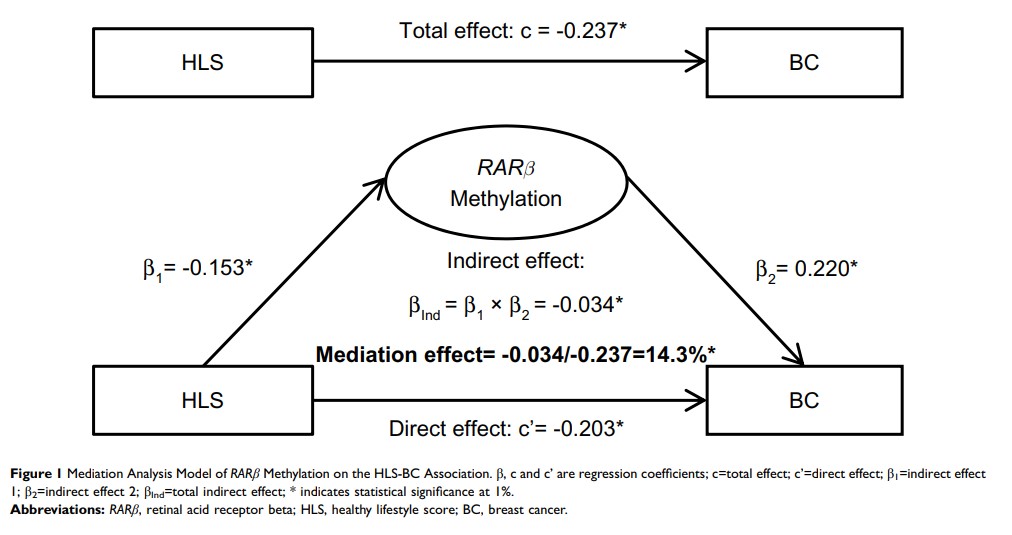
Results: A higher HLS was significantly associated with lower risk of BC (P -value< 0.001). In mediation analyses, the total effect of HLS on BC measured as a regression coefficient was significant (− 0.237). The indirect effects of HLS on RARβ methylation (− 0.153) and RARβ methylation on BC (0.220) were both significant. The significant mediation effect of RARβ methylation on the HLS-BC association was estimated at 14.3%.
Conclusion: The relationship between healthy lifestyle and BC is partly mediated by RARβ methylation, suggesting that epigenetic modifications play a role in the underlying mechanisms in response to lifestyles and contribute to the development of BC.
Keywords: healthy lifestyle score, retinoic acid receptor β, mediation effect, population study