110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

气象变量对急性缺血性卒中发作的潜在影响
Authors Qi X, Wang Z, Xia X, Xue J, Gu Y, Han S, Wang L, Li X, Leng SX
Received 12 March 2020
Accepted for publication 27 May 2020
Published 19 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 615—621
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S253559
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Marco Carotenuto
Purpose: The effects of meteorological parameters on stroke occurrence remain debated. The aim of the study was to assess the association between meteorological parameters and ischemic stroke onset in cold seasons in Tianjin.
Patients and Methods: Patients with acute ischemic stroke (946) were identified by standard sampling from one stroke unit in the Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China, from 10/1/2014 to 4/30/2019. Generalized linear Poisson regression models were used to explore the effect of meteorological parameters (air temperature, barometric pressure, and relative humidity) on daily ischemic stroke onset after adjusting for air pollutants, day of week, and public holiday.
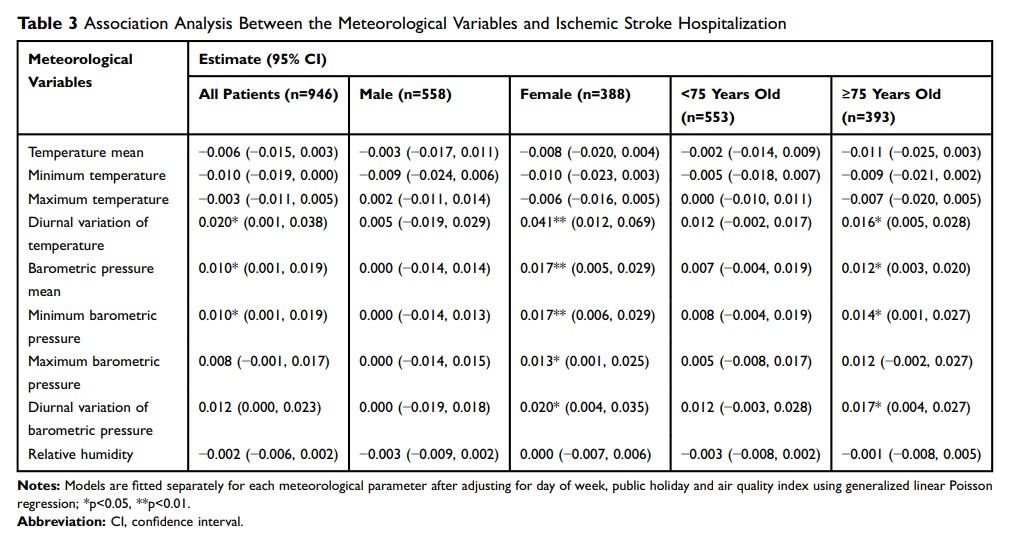
Results: The results showed that ischemic stroke onset was positively associated with the diurnal variation of temperature (β coefficient: 0.020, 95% CI [0.001, 0.038] p< 0.05). Significant positive correlation between ischemic stroke onset and barometric pressure (mean, minimum) was found (β coefficient: 0.010, 95% CI [0.001,0.019] p< 0.05; 0.010, 95% CI [0.001,0.019] p< 0.05). The subgroup analysis considering age and gender difference showed that the older and the female were more vulnerable to weather conditions.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that there was a measurable effect of weather parameters on daily ischemic stroke onset in colder seasons, suggesting that meteorological variables may, at least in part, play as risk factors for ischemic stroke onset, especially for the aging and female population.
Keywords: cold temperature, air pressure, ischemic stroke