110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

TDO 促进肝细胞癌进展
Authors Li S, Li L, Wu J, Song F, Qin Z, Hou L, Xiao C, Weng J, Qin X, Xu J
Received 8 March 2020
Accepted for publication 25 May 2020
Published 19 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 5845—5855
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S252929
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
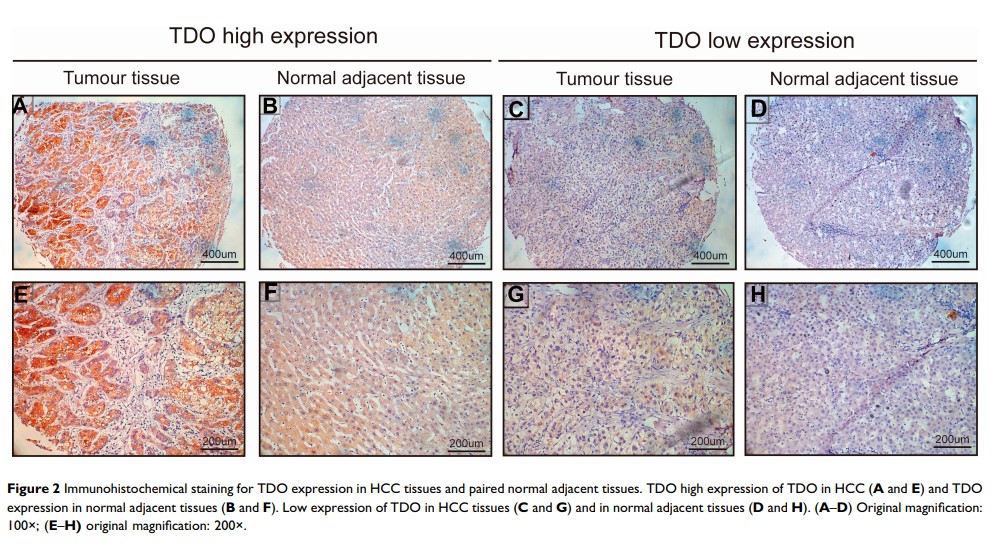
Purpose: Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO), encoded by the gene TDO2, is an enzyme that catalyses the first and rate-limiting step of tryptophan (Try) degradation in the kynurenine (Kyn) pathway in the liver. Recently, TDO has been demonstrated to be expressed in various human tumours, especially hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the role of TDO in HCC is still not very clear. Here, we studied the role of TDO in HCC.
Methods: We demonstrated that TDO is overexpressed in human HCC tissues and is significantly correlated with malignant phenotype characteristics, including tumour size, tumour differentiation, vascular invasion, etc. Kaplan–Meier analysis showed a poor overall survival rate in patients with TDO-overexpressing tumours. In addition, the effects of TDO on HCC tumour growth and metastasis were detected both in vivo and in vitro. TDO overexpression facilitated HCC cell growth, invasion and migration.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that TDO positively regulates HCC proliferation and invasion and acts as a new prognostic biomarker of HCC.
Keywords: TDO, tryptophan 2, 3-dioxygenase, hepatocellular carcinoma, tryptophan