110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对 Skp2 的抑制可使慢性髓细胞白血病细胞对伊马替尼敏感
Authors Chen X, Huang Z, Wu W, Xia R
Received 10 March 2020
Accepted for publication 13 May 2020
Published 22 June 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 4777—4787
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S253367
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
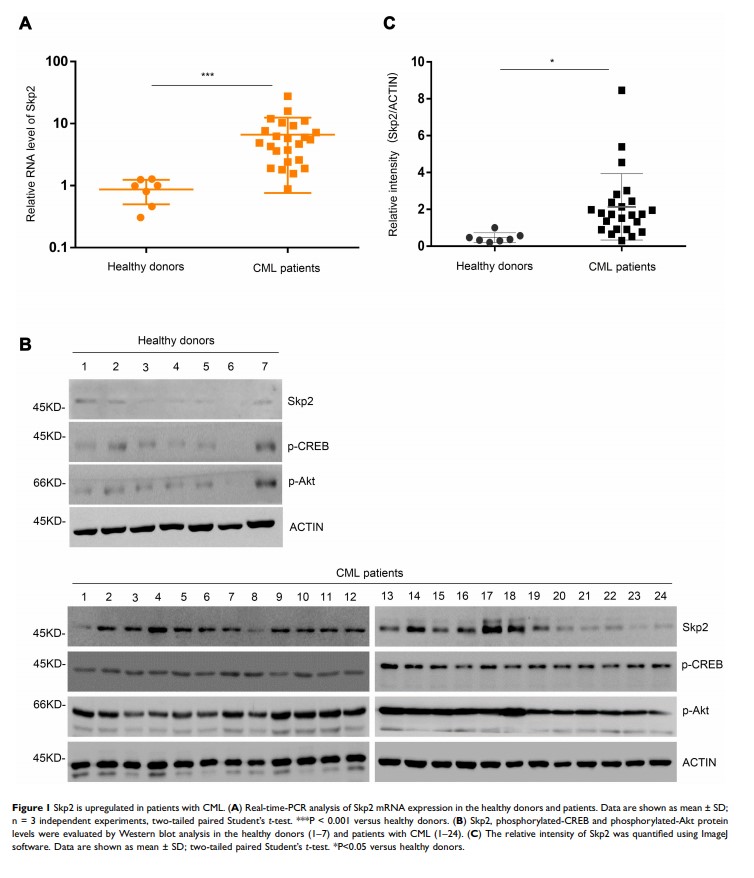
Introduction: Skp2 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that plays an important role in modulating tumor progression. The mechanisms underlying Skp2 in the promotion of proliferation and its function in the primary resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in human CML remain to be determined. This study aimed to investigate the function of Skp2 in CML progression as well as its effects on TKI sensitivity.
Methods: Expression of Skp2 in leukocytes from patients with CML and normal blood samples was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Cell proliferation was analyzed by EdU incorporation and cell counting assays. Luciferase reporter and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were used for examination of the effects of CREB on Skp2 expression. The apoptosis in vitro of K562 cells was analyzed by MTT and caspase 3/7 activity assays.
Results: The present study demonstrates that Skp2 was expressed at a higher level in patients with CML compared with healthy donors, and the elevated expression of Skp2 is critical for CML cell proliferation. Mechanistically, Skp2 was transcriptionally upregulated by CREB responsive to the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Furthermore, inhibition of Skp2 expression by shRNAs or blocking the PI3K/Akt/CREB pathway greatly enhances the sensitivity of CML cells to Imatinib treatment.
Conclusion: We conclude that the PI3K/Akt/CREB axis regulates the sensitivity of K562 cells to Imatinib via mediating Skp2 expression. The present study revealed an unknown role of Skp2 in CML progression and provided new aspects on the Skp2-modulated TKI sensitivity in CML, contributing to the development of potential therapeutic anticancer drugs.
Keywords: Skp2, PI3K/Akt, CREB, Imatinib