110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

身体形态指标与 2 型糖尿病发生风险之间的线性关系:基于在日本的回顾性队列研究的次级分析
Authors Zhao W, Tong JJ, Cao YT, Li JH
Received 29 March 2020
Accepted for publication 8 June 2020
Published 22 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2139—2146
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S256031
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Konstantinos Tziomalos
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the association between a body shape index (ABSI) and incident type 2 diabetes and to explore the shape of their relationship in a cohort of Japanese adults.
Patients and Methods: Data from 15,462 Japanese adults aged 18– 79 years attending the NAGALA study (NAfld in the Gifu Area, Longitudinal Analysis) were used. Body weight, height, and waist circumference were measured. Blood samples were measured for serum lipid, glucose, and HbA1c. The risk of incident type 2 diabetes according to ABSI was estimated using multivariate Cox regression models. We examined a potential nonlinear relationship using a smoothing function analysis. Subgroup analyses were conducted according to age, gender, smoking status, alcohol intake, fatty liver, and BMI.
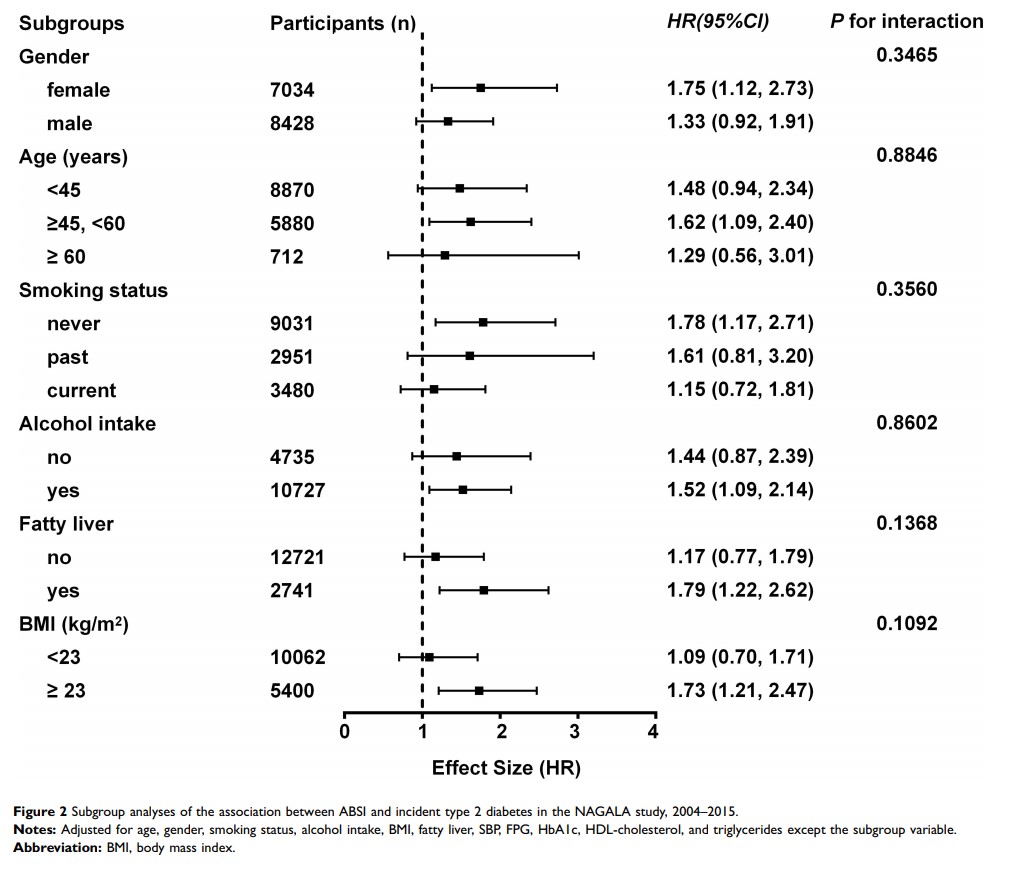
Results: After adjusting for potential confounding factors (age, gender, smoking status, alcohol intake, fatty liver, systolic blood pressure, BMI, fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c, HDL-cholesterol, triglycerides), a linear relationship was observed between ABSI and risk of type 2 diabetes. The hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) for incident type 2 diabetes with ABSI (10− 2 m11/6kg− 2/3) were 1.51 (1.13, 2.01) (p =0.005). When ABSI was handled as categorical variable, the HRs and 95% CIs in the quartile 2 to 4 versus the quartile 1 were 0.97 (0.67, 1.41), 1.21 (0.85, 1.72) and 1.30 (0.92, 1.83), respectively (P for trend = 0.046). Subgroup analyses showed that the association stably existed in different subgroups including gender, age, smoking status, alcohol intake, fatty liver, and BMI.
Conclusion: ABSI was linearly associated with an elevated risk of incident type 2 diabetes across the full range of ABSI, independent of gender, age, smoking status, alcohol intake, fatty liver, SBP, BMI, FPG, HbA1c, HDL-cholesterol, and triglycerides.
Keywords: ABSI, type 2 diabetes, linear relationship, a retrospective cohort study