110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

乳糖基化的 IR820/DOX 共组装纳米药物用于协同抗肿瘤治疗
Authors Jiang Y, Huang C, Luan Y
Received 29 January 2020
Accepted for publication 25 May 2020
Published 22 June 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 4431—4440
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S247617
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Introduction: Synergistic treatment integrating photothermal therapy (PTT) and chemotherapy is a promising strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the most commonly used photothermal agent, IR820, and chemotherapeutic drug, doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX), are both hydrophilic molecules that suffer from the drawbacks of a short circulation time, rapid elimination and off-target effects.
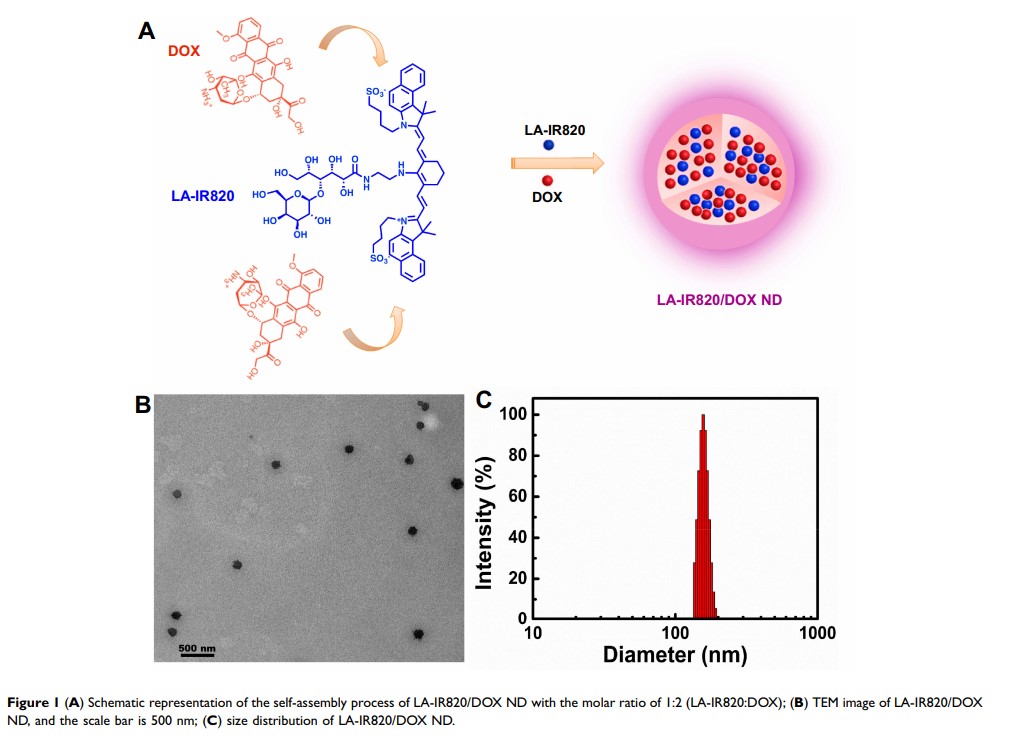
Methods and Results: Herein, a novel nanodrug that combined HCC-targeted IR820 and DOX was developed based on excipient-free co-assembly. First, lactosylated IR820 (LA-IR820) was designed to target HCC. Then, the LA-IR820/DOX nanodrug (LA-IR820/DOX ND) was purely self-assembled without excipient assistance. The physicochemical properties and the chemo-photothermal antitumour activity of the excipient-free LA-IR820/DOX ND were evaluated. More importantly, the obtained LA-IR820/DOX ND exhibited 100% drug loading, remarkable HCC targeting and excellent antitumour efficacy.
Conclusion: This excipient-free LA-IR820/DOX ND may be a promising candidate for the synchronous delivery and synergistic targeting of IR820 and DOX as a combined chemo-photothermal therapy.
Keywords: excipient-free, hepatoma cell targeting, self-assembly nanodrug, photothermal therapy, chemotherapy