110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血清 BDNF 水平与非惊厥性电疗法的抗抑郁作用无关
Authors Zheng W, Jiang ML, He HB, Li RP, Li QL, Zhang CP, Zhou SM, Yan S, Ning YP, Huang X
Received 31 March 2020
Accepted for publication 6 June 2020
Published 22 June 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 1555—1560
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S256278
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jun Chen
Objective: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has been implicated in the pathophysiology of depression and in the antidepressant response. This study examined whether changes in serum BDNF levels are associated with the antidepressant effects of nonconvulsive electrotherapy (NET).
Methods: For BDNF analyses, serum samples were collected from 20 patients with treatment-refractory depression (TRD) and from 20 healthy controls. Serum samples were also collected from patients following a course of NET.
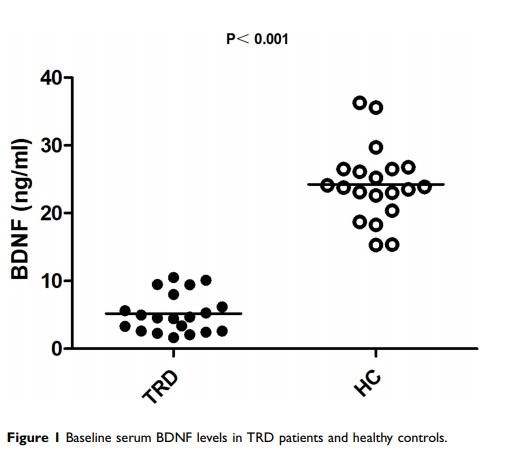
Results: Although significantly lower baseline serum BDNF levels were observed in TRD patients than in healthy controls, no changes in serum BDNF levels were found in TRD patients after a course of NET compared to baseline. No significant association was found between serum BDNF levels and depression severity.
Conclusion: Serum BDNF levels appear to have no clinical utility in the prediction of the antidepressant effects of NET in patients with TRD. Future studies of higher quality and with larger sample sizes are needed to confirm these findings.
Keywords: brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nonconvulsive electrotherapy, treatment-refractory depression