110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Aurora-B 通过激活 NPM1/ERK/NF-κβ/MMPs 轴促进骨肉瘤细胞生长和转移
Authors Song H, Zhou Y, Peng A, Liu J, Wu X, Chen W, Liu Z
Received 7 March 2020
Accepted for publication 10 May 2020
Published 23 June 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 4817—4827
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S252847
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
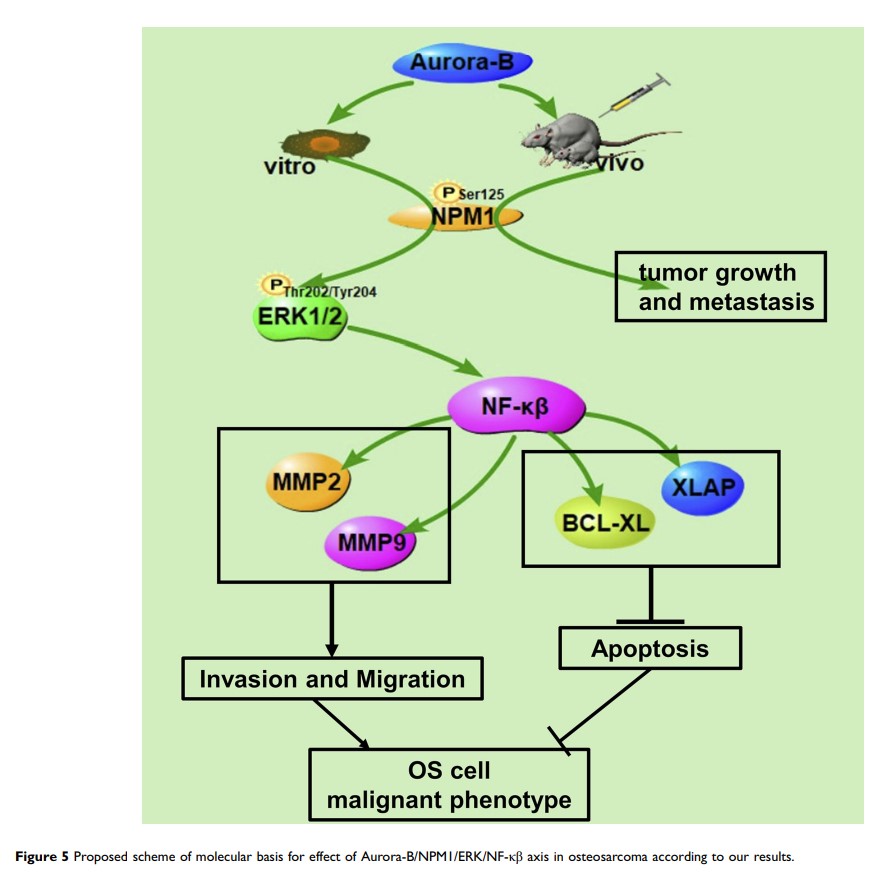
Purpose: Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common primary malignant tumor of the bone in young adolescents and children. We explored the underlying mechanism of Aurora-B in promoting OS cell proliferation and metastasis.
Patient and Methods: Bioinformatics was employed to predict the substrate of Aurora-B. IHC and Western blot were used to confirm the correlation between Aurora-B and NPM1. ERK/NF-κβ pathway-related proteins were detected by Western blot and immunofluorescence (IF). CCK8, wound healing, transwell, and Tunel assays were used to identify the cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis potential. Spontaneous metastasis xenografts were established to confirm the role of Aurora-B and NPM1.
Results: Aurora-B promotes NPM1 phosphorylation on Ser125. The phosphorylation of NPM1Ser125 induced by Aurora-B activates the ERK/NF-κβ signaling. Further study revealed that Aurora-B promotes proliferation, migration and inhibits apoptosis via phosphorylating NPM1 in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: Aurora-B promotes OS malignancy via phosphorylating NPM1Ser125 and activating ERK/NF-κβ signaling.
Keywords: Aurora-B, osteosarcoma, NPM1, ERK, NF-κβ