110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

一种新型的肿瘤抑制因子 SPINK5 作为头颈部鳞状细胞癌患者的独立预后预测指标
Authors Lv Z, Wu K, Qin X, Yuan J, Yan M, Zhang J, Wang L, Ji T, Cao W, Chen W
Received 27 October 2019
Accepted for publication 25 April 2020
Published 23 June 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 4855—4869
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S236266
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Background: In our previous study, serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 5 (SPINK5), which encodes the product of serine protease inhibitor lymphoepithelial Kazal-type-related inhibitor (LEKTI) was found to be down-regulated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) using oligonucleotide microarrays. However, the function and clinical implications of SPINK5/LEKTI remain obscure in HNSCC.
Methods: The endogenous expression level of SPINK5/LEKTI was further verified in 9 HNSCC cell lines and HNSCCs by means of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, real-time PCR, Western blotting and immunohistochemistry. The biological function of SPINK5/LEKTI was investigated in vitro and in vivo experiments. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazards regression model were used to determine the correlation between SPINK5/LEKTI expression and clinical outcome.
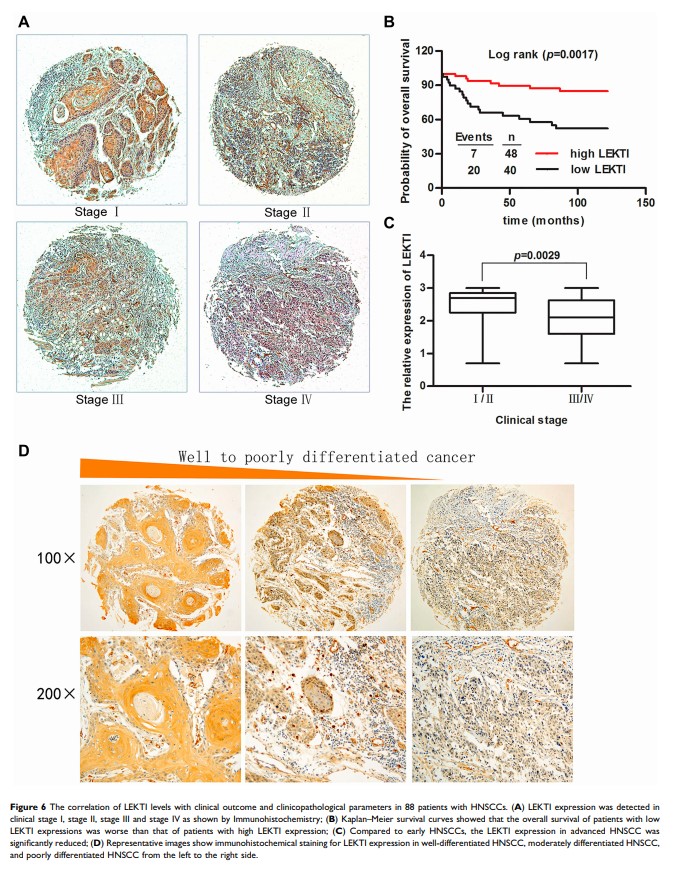
Results: Down-regulation expression of SPINK5/LEKTI was found in six out of nine HNSCC cell lines and in 85.7% HNSCC specimens (P < 0.0001). Upon silencing of SPINK5/LEKTI, the cell proliferation, plate colony formation and cell invasion of WU-HN6 cells were significantly increased, while exogenous overexpression of SPINK5/LEKTI, the proliferation, plate colony and invasion of WU-HN13 and HN30 cells were remarkably inhibited with the arrest of G1 cell cycle (P =0.0001, P =0.003, respectively). HNSCC patients with lower LEKTI levels had significantly inferior overall survival compared to those patients with higher LEKTI (P =0.0017) by Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression model analysis revealed that LEKTI expression was an independent prognostic predictor for HNSCC patients (HR=0.114, 95% CI:0.044– 0.292, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that SPINK5/LEKTI might be a tumor suppressor in HNSCCs and serve as an independent prognostic predictor for HNSCC patients.
Keywords: SPINK5/LEKTI, biological function, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, prognostic predictor