110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Apelin 通过激活 Nrf2 信号可减轻糖尿病大鼠的肾缺血再灌注损伤
Authors Zhang X, Zhu Y, Zhou Y, Fei B
Received 20 January 2020
Accepted for publication 23 March 2020
Published 23 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2169—2177
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S246743
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Konstantinos Tziomalos
Objective: Renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is commonly seen in diabetic patients. Apelin has been demonstrated to protect against renal I/R injury, whereas detailed modulatory mechanisms by which Apelin exerts its role in renal I/R injury in diabetic patients remain unclarified. This research aimed to probe the functional molecules under the regulation of Apelin in renal I/R injury in diabetic rats.
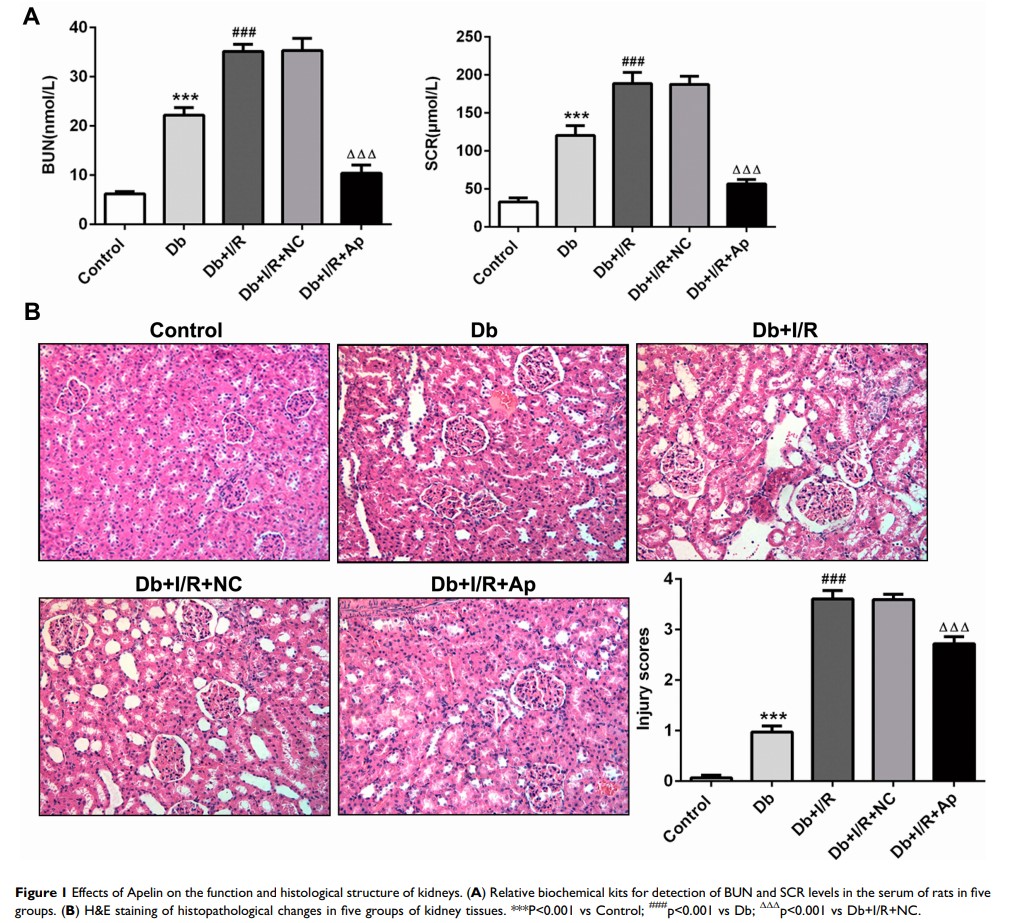
Materials and Methods: First, animal models were established for subsequent assays. Biochemical kits measured the serum levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (SCR), and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining examined the histopathological changes of kidney tissues. Inflammatory factors containing tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 1β (IL-1β), interleukin 6 (IL-6) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) were tested through enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), respectively. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in the serum and kidney tissues were separately assessed by specific ROS kits. Cell apoptosis was further estimated through terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and Western blot analysis. Eventually, the influences of Apelin on nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) and its downstream genes were explored via Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry (IHC).
Results: In the present study, Apelin ameliorated the damage to renal function and histological structure, decreased levels of inflammatory factors and ROS, and hampered cell apoptosis in renal I/R injury of diabetic rats. Moreover, Apelin could elevate the levels of Nrf2 and downstream genes which were decreased under renal I/R injury.
Conclusion: These data indicated that Apelin inhibited renal I/R injury through regulating Nrf2 signaling in diabetic rats, which might shed new light on the treatment of renal I/R injury in diabetic patients.
Keywords: renal ischemia/reperfusion injury, diabetes, Apelin, Nrf2 signaling