110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

类风湿关节炎患者和医师对治疗的满意度:以中国人群为基础的研究
Authors Jiang N, Yang P, Liu S, Li H, Wu L, Shi X, Fang Y, Zhao Y, Xu J, Jiang Z, Wu Z, Duan X, Wang Q, Tian X, Li M, Zeng X
Received 26 September 2019
Accepted for publication 14 March 2020
Published 23 June 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1037—1047
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S232578
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by chronic destructive synovitis and possible multisystem involvement. This study aimed to survey the treatment satisfaction of physicians and patients with RA, and to explore the potential factors.
Patients and Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted in 12 centers across China between March 2018 and April 2018. The Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire for Medication version II was used to assess the treatment satisfaction of patients and physicians. Multivariable regression analysis was used to determine the factors independently associated with treatment satisfaction of patients.
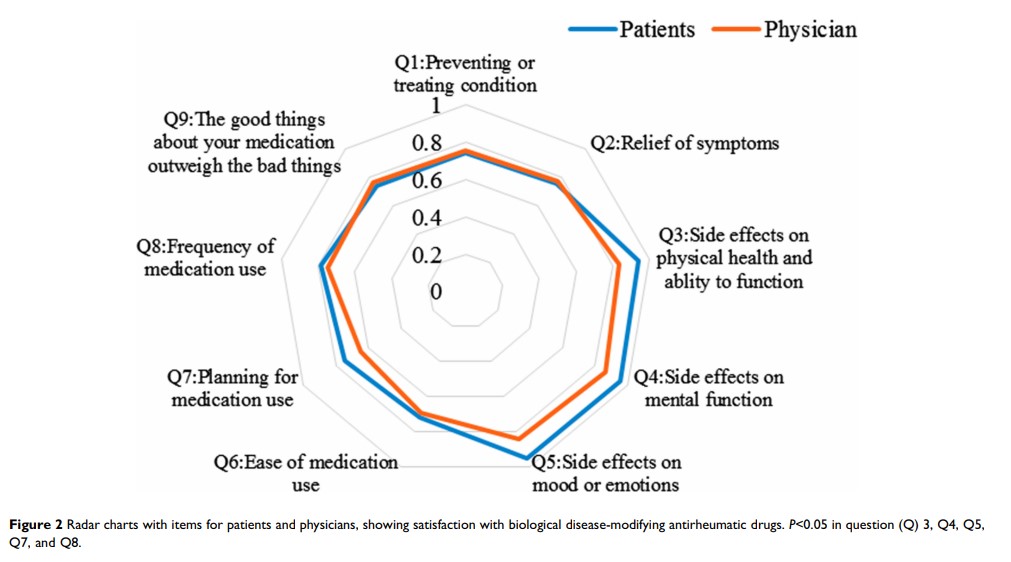
Results: The patients’ satisfaction (n=335) with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) was higher than physicians’ satisfaction (n=146) regarding the side effects (95.0± 14.3 vs 84.6± 15.7, P< 0.001) and convenience (74.6± 21.2 vs 69.1± 16.5, P=0.002). Among physicians, global satisfaction with bDMARDs was higher than that with conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs). The multivariable regression analysis showed that age was positively associated with satisfaction of patients, while college or above education and self-assessment of disease severity were inversely associated with satisfaction. Treatment satisfaction was associated positively with the quality of communication with the physician and inversely with treatment costs.
Conclusion: For bDMARDs, the treatment satisfaction of patients with RA is generally higher than that of physicians’. Physicians’ satisfaction with bDMARDs is higher than with csDMARDs. Age, education, disease severity, communication with the physician, and treatment costs are independently associated with the treatment satisfaction among patients. Physician–patient communication should be improved in clinical practice. Treatment costs should be taken into account when physicians make decisions.
Keywords: patient, physician, rheumatoid arthritis, treatment satisfaction, TSQM-II