110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对于高同型半胱氨酸血症大鼠,纳米硒在体内外具有抗氧化剂和抗内皮功能障碍特性
Authors Zheng Z, Liu L, Zhou K, Ding L, Zeng J, Zhang W
Received 31 March 2020
Accepted for publication 25 May 2020
Published 23 June 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 4501—4521
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S255392
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Purpose: Elevation of blood homocysteine (Hcy) level (hyperhomocysteinemia) is a risk factor for cardiovascular disorders and is closely associated with endothelial dysfunction. The present study aims to investigate the protective effect and underlying mechanism of nanoscale selenium (Nano-Se) in Hcy-mediated vascular endothelial cell dysfunction in vitro and in vivo.
Materials and Methods: By incubating vascular endothelial cells with exogenous Hcy and generating hyperhomocysteinemic rat model, the effects of Nano-Se on hyperhomocysteinemia-mediated endothelial dysfunction and its essential mechanisms were investigated.
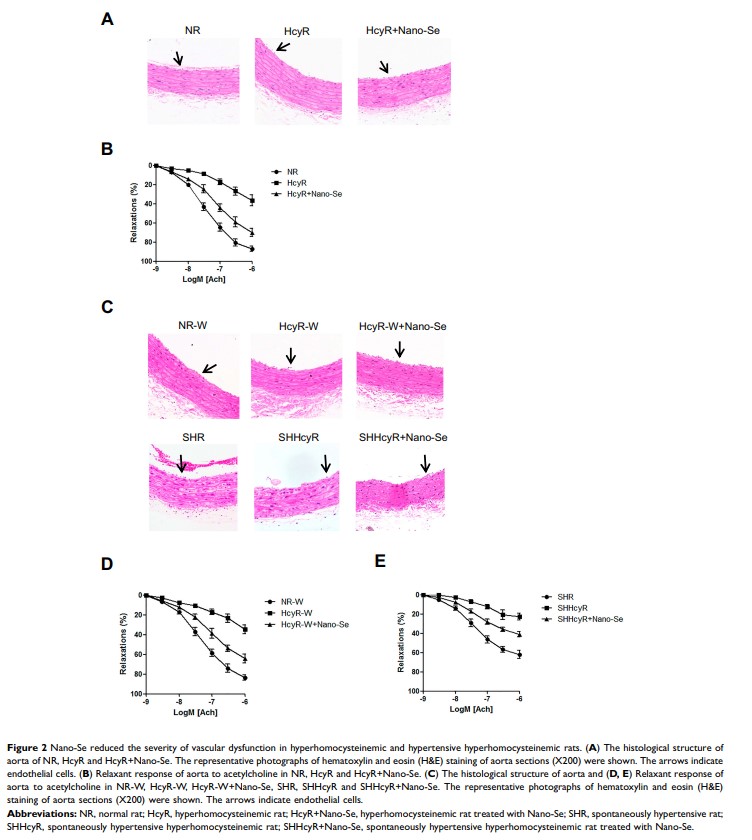
Results: Nano-Se inhibited Hcy-induced mitochondrial oxidative damage and apoptosis by preventing the downregulation of glutathione peroxidase enzyme 1 and 4 (GPX1, GPX4) in the vascular endothelial cells, thus effectively prevented the vascular damage in vitro and in vivo in the hyperhomocysteinemic rats. Nano-Se possessed similar protective effects but lower toxicity against Hcy in vascular endothelial cells when compared with other forms of Se.
Conclusion: The application of Nano-Se could serve as a novel promising strategy against Hcy-mediated vascular dysfunction with reduced risk of Se toxicity.
Keywords: nano-selenium, Nano-Se, homocysteine, endothelium dysfunction, glutathione peroxidase enzymes, GPXs, reactive oxygen species, ROS