110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

核糖体蛋白 RPS21 的下调通过 MAPK 信号通路失活抑制骨肉瘤细胞的侵袭行为
Authors Wang T, Wang ZY, Zeng LY, Gao YZ, Yan YX, Zhang Q
Received 22 January 2020
Accepted for publication 27 May 2020
Published 25 June 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 4949—4955
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S246928
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objective: The goal of our present study was to explore the expression level, biological function, and underlying molecular mechanism of ribosomal protein s21 (RPS21) in human osteosarcoma (OS).
Methods: Firstly, we evaluated the expression of RPS21 in OS tissue samples based on the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets and also measured the RPS21 expression of OS cell lines (MG63, and U2OS) by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). siRNA interference method was used to reduce the expression of RSP21 in the OS cells. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), colony formation, wound-healing, and transwell assays were conducted to measure the proliferation, migration, and invasion of OS cells. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway-related proteins levels were examined by Western blot.
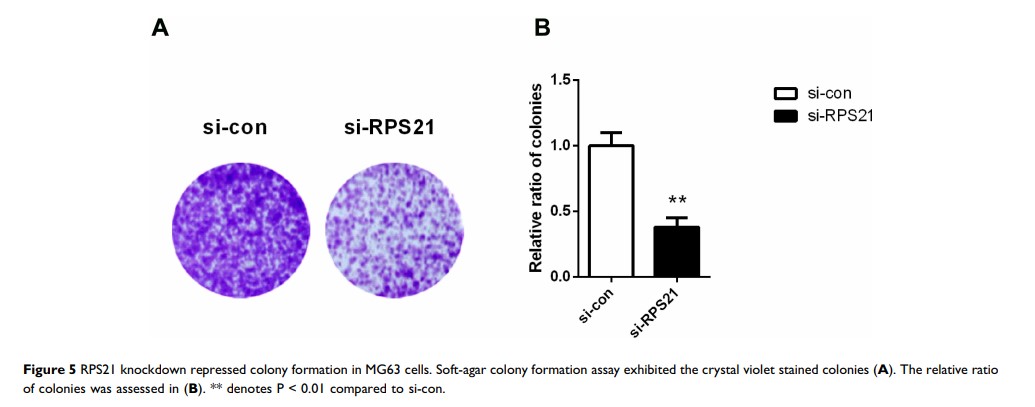
Results: Our analyses showed that the expression of RPS21 was significantly increased in OS, compared with normal samples. Upregulation of RPS21 was associated with worse outcomes of OS patients. Knockdown of RPS21 suppressed OS cell proliferation, colony-forming ability, migration, and invasion capacities. Moreover, down-regulation of RPS21 inactivated the MAPK signaling pathway.
Conclusion: RPS21 plays an oncogenic candidate in OS development via regulating the activity of MAPK pathway; therefore, it may serve as a novel therapeutic target for OS treatment.
Keywords: RPS21, MAPK pathway, osteosarcoma, viability, migration