110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对于接受 R-CHOP 治疗的原发性胃弥漫性大 B 细胞淋巴瘤患者,PD-L1 和 miR-34a 是其预后因素
Authors Wang J, Shang S, Li J, Deng H, Ouyang L, Xie H, Zhu H, Li Y, Zuo C
Received 31 January 2020
Accepted for publication 10 June 2020
Published 25 June 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 4999—5008
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S247874
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Introduction: Primary gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (GDLBCL) is a heterogeneous disease in clinicopathological features and prognosis. Programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) and microRNA-34a (miR-34a) play crucial roles in GDLBCL progress. The purpose of this research is to explore the clinical significance of PD-L1 and miR-34a expression in GDLBCL.
Patients and Methods: The expressions of PD-L1 and miR-34a were examined by IHC and qRT-PCR in 109 patients who were diagnosed with GDLBCL and were treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, prednisone vincristine and prednisone chemotherapy (R-CHOP) from January 2010 to December 2018.
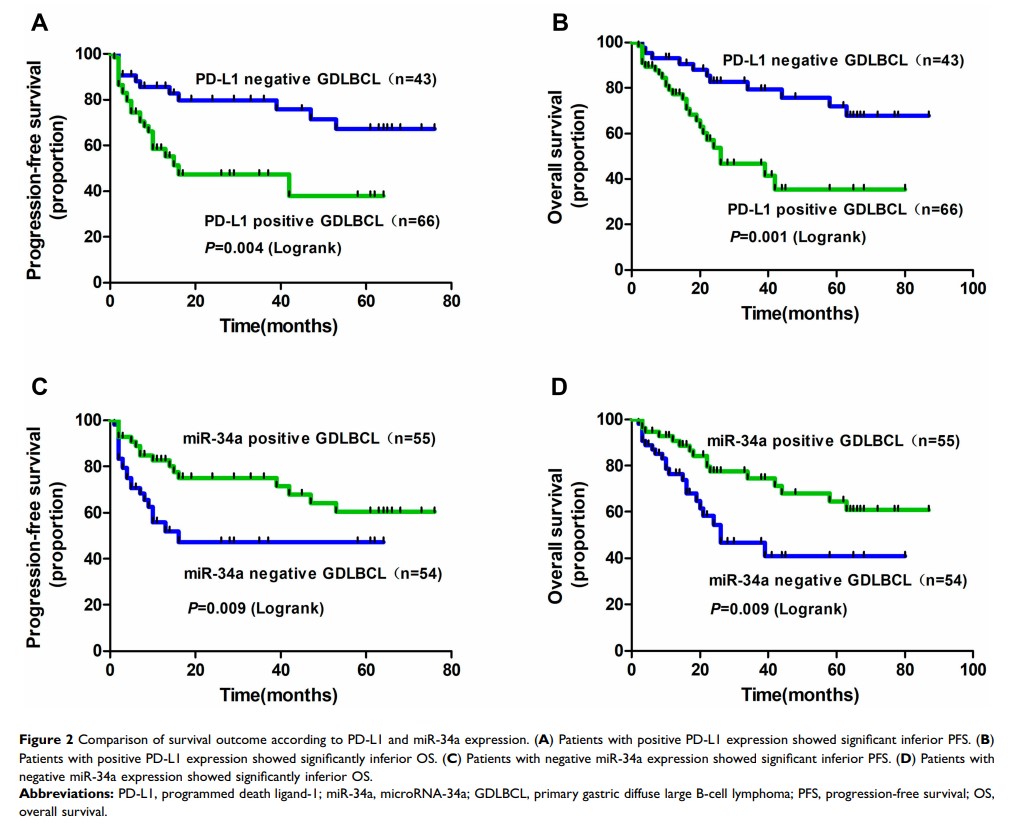
Results: PD-L1 level was significantly higher in tumor tissues than adjacent non-tumor tissues (60.5%, P < 0.001), while the miR-34a level was just reversed (50.5%, P < 0.001), which was negatively correlated (r =− 0.524, P < 0.001). Notably, PD-L1-positive and miR-34a-negative expressions were significantly correlated with the advanced Lugano stage of IIE-IV stage (P < 0.001 and P < 0.01), elevated serumal LDH levels (P < 0.001 and P < 0.05), B symptoms present (P < 0.001 and P < 0.001), non-GCB subtype (P < 0.001 and P < 0.001) and negative Bcl-2 expression (P < 0.05 and P < 0.001). PD-L1 high and miR-34a low expression groups had more patients with IPI scores of 2 or greater (P < 0.001 and P < 0.05) and poor R-IPI (P < 0.01 and P < 0.01). The complete response rate was upregulated in patients with negative PD-L1 and positive miR-34a expression after R-CHOP treatment.
Discussion: PD-L1 expression and miR-34a expression were significantly associated with clinicopathological characteristics and survival prognosis; they may serve as novel prognostic markers in GDLBCL patients who were treated with R-CHOP. Immunotherapies targeting PD-L1 and miR-34a pathway may have therapeutic potential in GDLBCL.
Keywords: GDLBCL, R-CHOP, PD-L1, miR-34a, tumor immunotherapy