110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LOXL1-AS1 通过调节 miR-3128/RHOXF2 轴促进非小细胞肺癌进展
Authors Zhao L, Zhang X, Guo H, Liu M, Wang L
Received 31 January 2020
Accepted for publication 23 April 2020
Published 25 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 6063—6071
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S247900
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate the molecular mechanism of LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: Lung cancer cell lines (H1299, A549, H520 and H596) and human normal lung epithelial cell line (BEAS-2B) were used in this study. Gene expression was measured by qRT-PCR (quantitative real-time PCR). The bioinformatics databases (miRDB and TargetScan7) were used to predict target genes. Luciferase assay and pull-down assay were processed for verifying the binding sites. CCK8 assay was used for detecting proliferation, and transwell assay was undertaken for migration and invasion.
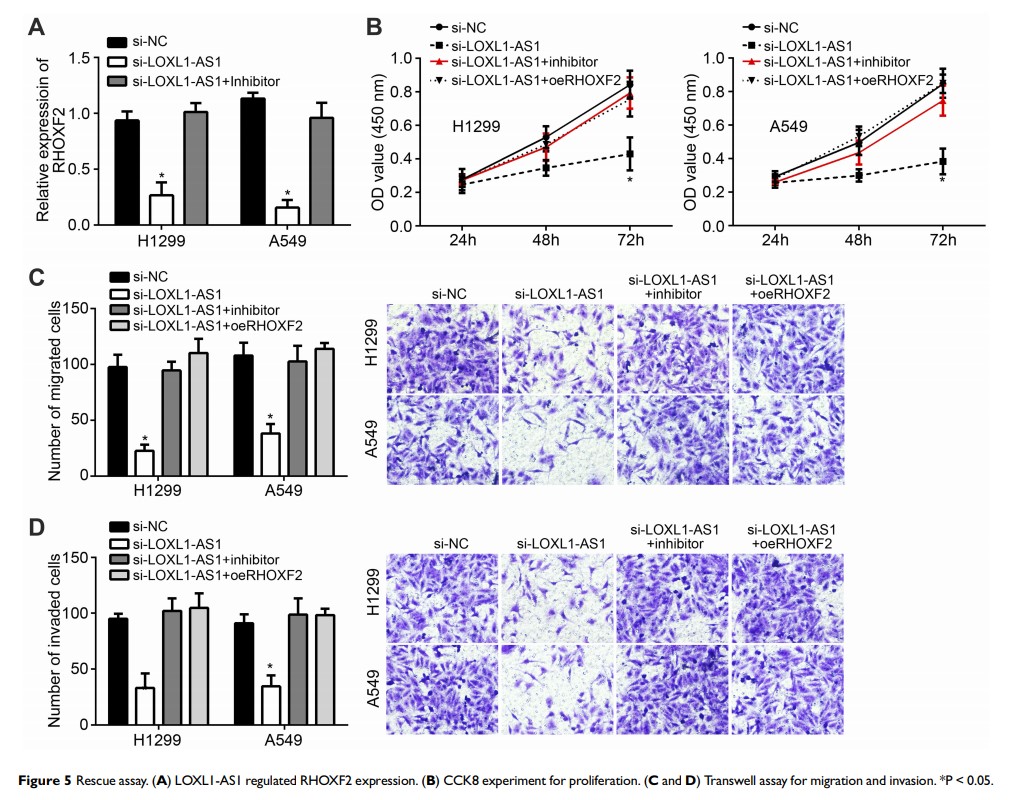
Results: LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 was higher expressed in lung cancer tissues and cells. Moreover, LOXL1-AS1 expression was upregulated in tumor tissues with advanced stages and metastasis. After knocking down LOXL1-AS1, proliferation, invasion and migration of H1299 and A549 cells were inhibited. Interestingly, miR-3128 was negatively regulated by LncRNA LOXL1-AS1, which inhibited the expression of RHOXF2. Rescue assay also confirmed that miR-3128 inhibitor and oeRHOXF2 could rescue the effect of down-regulated LOXL1-AS1 on proliferation, invasion and migration progression.
Conclusion: LOXL1-AS1 promotes the progression of NSCLC by regulating miR-3128/RHOXF2 axis, which might be a new potential target for the diagnosis and treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: NSCLC, LOXL1-AS1, miR-3128, RHOXF2