110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

分离自中国三级医院的脓肿分枝杆菌复杂临床菌株的抗菌药物敏感性
Authors Guo Y, Cao X, Yu J, Zhan Q, Yang J, Wu X, Wan B, Liu Y, Yu F
Received 4 March 2020
Accepted for publication 9 June 2020
Published 26 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2001—2010
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S252485
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Introduction: Mycobacterium abscessus complex (MABC) is a group of important infectious agents that are highly associated with drug resistance, and antibiotic treatment is usually ineffective. This study investigated the characteristics of antimicrobial susceptibility of MABC isolates and the synergy between certain β-lactam combinations against MABC infection.
Methods: We collected 129 MABC isolates from patients with lower respiratory tract infections and categorized them into three subspecies. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 15 antimicrobials for the MABC isolates were determined using commercial Sensititre RAPMYCOI MIC plates and the broth microdilution method, as recommended in the CLSI (M24-A2). In addition, the MICs of imipenem, alone and with ceftazidime and/or avibactam, were assessed in vitro for all isolates. The erm (41) and rrl genes were also sequenced.
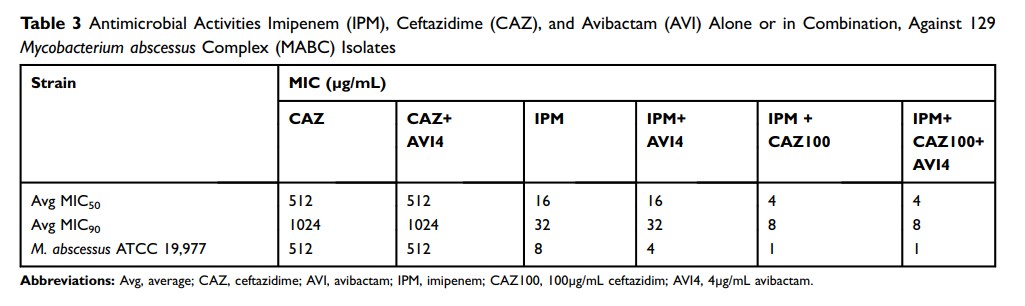
Results: The MABC isolates exhibited > 80% resistance to 11 of the 15 antimicrobials. Regarding the remaining four antimicrobials, the isolates were least resistant to tigecycline (12.4%) and amikacin (3.9%), and only partially resistant to two cefoxitin (39.5%) and imipenem (40.3%). Compared with M. massiliense isolates, M. abscessus and M. bolletii isolates were more resistant to amikacin and imipenem, whereas M. abscessus was significantly less resistant to tigecycline relative to M. massiliense and M. bolletii isolates. The clarithromycin inducible resistance rate was 68.4% and 74.3% among M. bolletii and M. abscessus isolates. Furthermore, 88.7% of the M. abscessus isolates carried a T at position 28 of erm (41), which is associated with inducible clarithromycin resistance. In addition, compared to imipenem with avibactam only, the MIC50 and MIC90 values of imipenem after adding ceftazidime plus avibactam were decreased fourfold.
Conclusion: The antimicrobial resistance rates and the characteristics of the erm (41) gene associated with inducible clarithromycin resistance were different among the three MABC subspecies. There was also synergy between imipenem and 100μg/mL ceftazidime against MABC isolates.
Keywords: Mycobacterium abscessus complex, resistance, erm (41), synergy, dual β-lactam therapy