110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

来自中国中部武汉的金黄色葡萄球菌分离株的分子特性、抗菌素耐药性和毒力基因谱
Authors Fu Y, Xiong M, Li X, Zhou J, Xiao X, Fang F, Cheng X, Le Y, Li Y
Received 15 February 2020
Accepted for publication 9 June 2020
Published 30 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2063—2072
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S249988
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the molecular characteristics, antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes profiles of S. aureus isolates from Wuhan, central China.
Materials and Methods: A total of 302 non-duplicate S. aureus isolates were collected successively during January–December 2018 and subjected to multi-locus sequence typing (MLST), staphylococcal protein A (spa ) typing and Panton–Valentine leucocidin (PVL) and staphylococcal enterotoxin A, B, C, D, E, G, H and I (sea, seb, sec, sed, see, seg, seh and sei ) detection. All methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) isolates were additionally subjected to staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec (SCCmec ) typing.
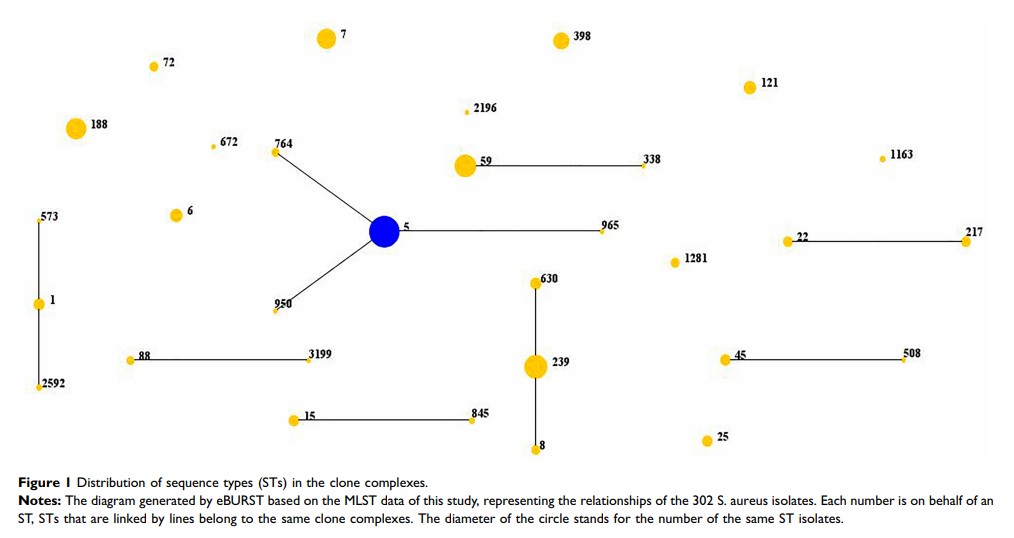
Results: Of the 302 S. aureus isolates, 131 were categorised as MRSA, yielding a rate 1.4 times the average rate in China during 2018 (43.4% vs 30.9%). Thirty-one sequence types (STs) and 82 spa types were identified. The most prevalent clones were ST5-t2460 (10.9%), ST239-t030 (9.3%), ST188-t189 (7.9%) and ST59-t437 (6.3%). Notably, the continued prevalence of ST239-t030 in Wuhan differs from other areas in China. SCCmec types and subtypes I, II, III, IVa and V were present in 0.8%, 36.6%, 26.0%, 20.6% and 8.4% of MRSA isolates. A comprehensive analysis identified ST5-t2460-SCCmec II (25.2%,), ST239-t030-SCCmec III (19.8%) and ST59-t437-SCCmec IVa (7.6%) as the major clones among MRSA isolates. The genes pvl, sea, seb, sec, sed, see, seg, seh and sei were detected at respective frequencies of 11.9%, 42.1%, 49.7%, 45.0%, 20.9%, 33.8%, 60.5%, 25.8% and 66.9%.
Conclusion: ST239-t030 remains one of the most prevalent clones in S. aureus isolates from Wuhan, leading us to conclude that S. aureus isolates from Wuhan possess unique molecular characteristics. The S. aureus isolates also exhibit unique antimicrobial resistance profiles and harbour relatively high numbers of enterotoxin virulence genes, compared with other reports from China.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus , molecular characteristics, antimicrobial resistance, virulence